Introduction to Ozempic
Ozempic, which contains the active ingredient semaglutide, is a prescription medication used to treat type 2 diabetes and lower blood sugar levels in adults with type 2 diabetes. It is proven to lower blood sugar and A1C when used along with diet and exercise.
It is also used to reduce the risk of kidney function decline, kidney failure, and cardiovascular death in people with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease.
Ozempic is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist that mimics a natural hormone in the body to improve blood sugar control.

Image of Ozempic pen
Uses of Ozempic
Ozempic is used to treat type 2 diabetes and improve blood sugar control in adults. A majority of adults taking Ozempic reached an A1C under 7% and maintained it.
It is also used to lower the risk of major cardiovascular events such as heart attack, stroke, or death in adults with type 2 diabetes and known heart disease.
Additionally, Ozempic can help with weight loss, although it is not approved by the FDA for this purpose. Some doctors prescribe Ozempic off-label for weight management, but it is important to consult your healthcare provider as insurance may not cover off-label prescriptions.
Benefits of Ozempic
Ozempic can help lower blood sugar levels and improve glycemic control in people with type 2 diabetes. Some people lose weight while using Ozempic as part of their treatment for type 2 diabetes.
It can also reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, worsening kidney disease, and kidney failure in people with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. The significant weight loss experienced by some individuals can further improve blood sugar control and reduce the risk of other health problems.
Ozempic may also help with weight loss, which can further improve blood sugar control and reduce the risk of other health problems. Additionally, it has been shown to be effective at reducing body weight, making it a valuable option for patients looking to manage both their blood sugar levels and weight. Patients using Ozempic lost an average of 14 pounds over a 40-week period in clinical studies.
How Ozempic Works
Ozempic works by stimulating the pancreas to release more insulin after eating, preventing the liver from releasing stored sugars, and slowing down the movement of food through the body. Ozempic slows the movement of food through the digestive system, which can impact those with specific health conditions such as gastroparesis. It belongs to a group of drugs called GLP-1 agonists, which are specifically designed to treat type 2 diabetes.
Ozempic mimics a natural hormone known as GLP-1, which helps to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of serious health problems associated with type 2 diabetes. Ozempic works by stimulating insulin release, reducing glucose production in the liver, and slowing food digestion, all contributing to its effectiveness in weight management. The active ingredient in Ozempic, semaglutide, plays a crucial role in its effectiveness for weight management and blood sugar control.
Ozempic also slows down food digestion, which can help reduce appetite and lead to weight loss.
Mechanism of Action
Ozempic works by mimicking a natural hormone in the body called GLP-1, which plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. When you take Ozempic, it stimulates the pancreas to release more insulin after meals, which helps to lower blood sugar levels. Additionally, it reduces the release of glucagon, a hormone that raises blood sugar levels. This dual action helps to maintain a more stable blood sugar level throughout the day.
One of the unique aspects of Ozempic is its ability to slow down the movement of food from the stomach to the small intestine. This slower digestion process means that glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream more gradually, preventing spikes in blood sugar levels. For adults with type 2 diabetes, this can be particularly beneficial in managing their condition.
Moreover, Ozempic has been shown to reduce the risk of major cardiovascular events such as heart attack, stroke, and cardiovascular death in adults with type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease. It also offers protection against worsening kidney disease and kidney failure in those with chronic kidney disease. By addressing both blood sugar control and cardiovascular health, Ozempic provides a comprehensive approach to managing type 2 diabetes.
Dosage and Administration
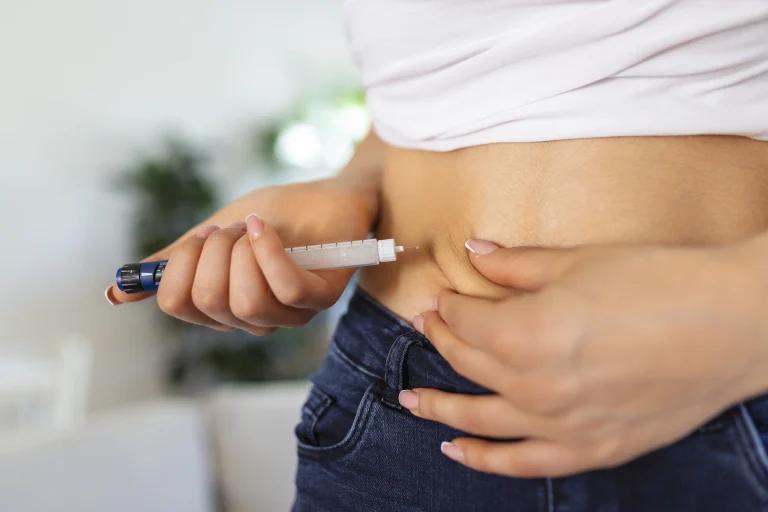
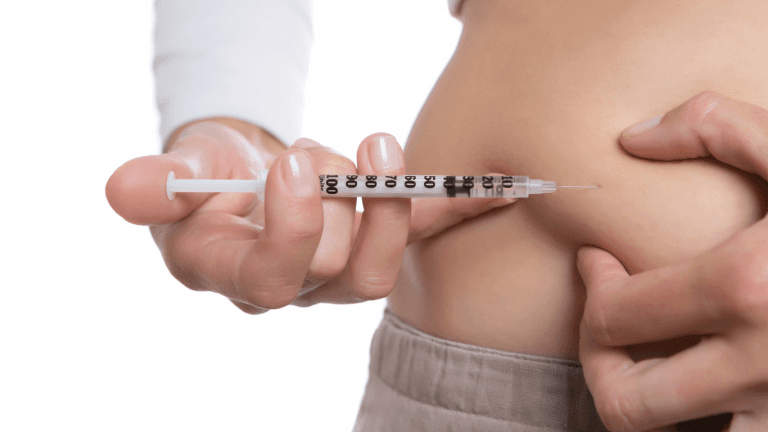
Ozempic is administered via subcutaneous injection once a week, making it a convenient option for many patients. The Ozempic pen comes in various strength options, including 0.5 mg and 1 mg, and includes specifics on its use, such as the number of needles included in each carton and guidelines for dosage and injection frequency. The typical starting dose is 0.5 mg injected subcutaneously once a week, which may be increased to a maintenance dose of 1 mg per week based on the individual’s response to treatment. Ozempic is administered as a subcutaneous injection in the thigh, abdomen, or upper arm. It should be injected once a week on the same day each week. A new needle should be used for each injection of Ozempic. If you miss a dose of Ozempic, it can be taken within 5 days of the missed dose. Ozempic should be stored in the refrigerator before use and can be kept at room temperature only after being used.
For patients with chronic kidney disease or kidney disease, close monitoring is essential while taking Ozempic. This is because the medication may increase the risk of worsening kidney disease or kidney failure. Regular check-ups and kidney function tests can help manage these risks effectively.
Side Effects of Ozempic
Common side effects of Ozempic include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach pain.
Serious side effects can include pancreatitis, thyroid tumors, and severe allergic reactions. If you experience severe pain, particularly in the abdomen, seek immediate medical help as it may indicate pancreatitis. Seek emergency medical help if you experience symptoms of an allergic reaction such as hives or difficulty breathing, and stop the medication immediately. It is crucial to recognize symptoms of a serious allergic reaction and seek immediate assistance if they occur.
Ozempic can also increase the risk of low blood sugar, especially when used with other diabetes medications. Trouble swallowing can be a symptom of thyroid tumors, so it is important to seek medical attention if you experience this symptom. Trials have revealed a link between Ozempic and the development of thyroid tumors, including the potential for thyroid cancer, specifically medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC).
Additionally, there is a risk of worsening diabetic retinopathy for patients undergoing treatment, particularly for those with existing diabetic eye disease.
Long-term Effects
Long-term use of Ozempic has been associated with several significant benefits, including improved blood sugar control and weight loss. Many patients find that their blood sugar levels become more stable over time, reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes. Additionally, the weight loss experienced by some patients can further enhance blood sugar control and overall health.
However, it’s important to be aware of potential long-term side effects. Some patients may experience pancreatitis, a serious condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas. There is also a risk of developing thyroid cancer, particularly medullary thyroid carcinoma, which is why Ozempic is not recommended for individuals with a history of this condition or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2.
Severe stomach problems, such as persistent nausea and vomiting, can also occur with long-term use. In rare cases, Ozempic can cause serious allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis. Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly and adjusting the dosage as needed can help minimize the risk of low blood sugar. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should consult their healthcare provider before starting Ozempic treatment to ensure it is safe for them and their baby.
Drug Interactions with Ozempic
Ozempic can interact with other medications, including insulin, sulfonylureas, and other diabetes medications. It is important to report all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to healthcare providers to manage potential drug interactions effectively. It can also interact with certain antibiotics and other medications that affect the digestive system. Using too much Ozempic can be dangerous, leading to severe nausea and low blood sugar levels; immediate medical help should be sought if an overdose occurs. Drinking alcohol can also affect blood sugar levels and increase the risk of serious side effects when taking Ozempic.
Medical Conditions and Ozempic
Ozempic is not recommended for people with a history of pancreatitis, thyroid cancer, or medullary thyroid carcinoma.
It is also not recommended for people with severe stomach problems, kidney problems, or heart disease.
Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not take Ozempic, as it may affect the unborn baby or pass into breast milk. It is unknown if Ozempic passes into breast milk, so consult your healthcare provider regarding the implications of using Ozempic while breastfeeding. Ozempic may also cause gallbladder problems, such as cholecystitis and gallstones, so it is important to contact your healthcare provider if you experience related symptoms. Medications like Saxenda are used by people facing weight-related issues, including high cholesterol, underscoring the connection between these health concerns and effective treatment options. The American Diabetes Association recommends maintaining an A1C below 7% for adults with type 2 diabetes as part of their guidelines for diabetes management.
Lifestyle and Dietary Considerations
To maximize the benefits of Ozempic treatment, it is essential to adopt a healthy lifestyle and dietary habits. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help improve blood sugar control and overall health. Regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can also enhance the effectiveness of Ozempic and contribute to weight loss.
Patients should be mindful of the potential for increased risk of hypoglycemia, especially when taking Ozempic in combination with other diabetes medications. Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly can help detect and manage low blood sugar episodes. Drinking alcohol can also affect blood sugar levels and increase the risk of hypoglycemia, so it is advisable to limit alcohol consumption and discuss safe drinking guidelines with your healthcare provider.
For those who have undergone bariatric surgery, it’s important to note that this procedure may affect the absorption of Ozempic. Consult your healthcare provider to ensure that your treatment plan is adjusted accordingly. By maintaining a healthy diet, staying active, and monitoring blood sugar levels, you can optimize the benefits of Ozempic and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Ozempic and Interactions
Ozempic can interact with other drugs and medical conditions, including bariatric surgery, diet and exercise, and other health conditions. It is essential to inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and health conditions before starting Ozempic treatment to manage potential drug interactions effectively.
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, kidney function, and other health markers is also crucial when taking Ozempic. There are risks associated with Ozempic, particularly the potential for high blood sugar levels when patients reduce their insulin dosage too quickly. Additionally, it is important to drink fluids to prevent dehydration, especially if experiencing nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
Patient Experiences and Testimonials
Many patients have shared positive experiences with Ozempic, praising its effectiveness in lowering blood sugar levels and improving overall blood sugar control. Clinical studies evaluating the effectiveness of various diabetes medications, including Ozempic, have shown significant weight loss outcomes among adults, with specific statistics on patients lost illustrating the success of these treatments in managing obesity and diabetes. Some individuals have also reported experiencing weight loss while on Ozempic, which can be a beneficial side effect for those managing type 2 diabetes. The medication may lead to weight loss as a secondary effect due to decreased appetite and feelings of fullness, although Ozempic is not officially approved for weight loss and should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
While many patients have had positive outcomes, some have reported serious allergic reactions, including severe stomach problems and thyroid tumors. These experiences highlight the importance of being vigilant about potential side effects and seeking medical attention if any severe symptoms occur.
Comparisons with Other Medications
When compared to other diabetes medications like metformin and sulfonylureas, Ozempic has shown significant effectiveness in lowering blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. However, it’s important to note that Ozempic may carry a higher risk of serious side effects, such as pancreatitis and thyroid cancer, compared to some other medications. Additionally, Ozempic may increase the likelihood of food or liquid entering the lungs during surgical or medical procedures requiring anesthesia or deep sedation, so it is crucial to inform healthcare providers about the medication prior to surgery.
Ozempic has also been compared to other GLP-1 receptor agonists, such as liraglutide and dulaglutide. Clinical trials have demonstrated that Ozempic has a similar efficacy and safety profile to these medications. However, Ozempic may interact with other drugs, including over-the-counter medicines and prescription medications, which can affect its efficacy and safety. Always consult your healthcare provider about any other medications you are taking to avoid potential interactions.
Cost and Insurance Coverage
The cost of Ozempic can vary widely depending on your health insurance coverage and prescription medication plan. While Ozempic is typically covered by most insurance plans, including Medicare and Medicaid, the out-of-pocket cost can still be high for those without insurance coverage. For people with commercial or private insurance, Ozempic may cost as little as $25 for a one-month supply for up to 48 months. The retail price of Ozempic can be as high as $1,080 for a month supply depending on the pharmacy.
Patients can explore various cost-saving options, such as coupons and patient assistance programs, to help reduce the financial burden. It’s essential to discuss the cost and insurance coverage of Ozempic with your healthcare provider and health insurance provider to determine the best course of treatment.
Additionally, patients should be aware of the potential increased risk of serious side effects and interactions with other medications when taking Ozempic. Carefully following the prescribed dosage and administration instructions can help minimize these risks and ensure the best possible outcomes.
Conclusion
Ozempic is a valuable medication for managing type 2 diabetes. By following your recommended treatment plan and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, you can effectively control your blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of cardiovascular events, and improve your overall health.
NowPatient has taken all reasonable steps to ensure that all material is factually accurate, complete, and current. However, the knowledge and experience of a qualified healthcare professional should always be sought after instead of using the information on this page. Before taking any drug, you should always speak to your doctor or another qualified healthcare provider.
The information provided here about medications is subject to change and is not meant to include all uses, precautions, warnings, directions, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or negative effects. The absence of warnings or other information for a particular medication does not imply that the medication or medication combination is appropriate for all patients or for all possible purposes.