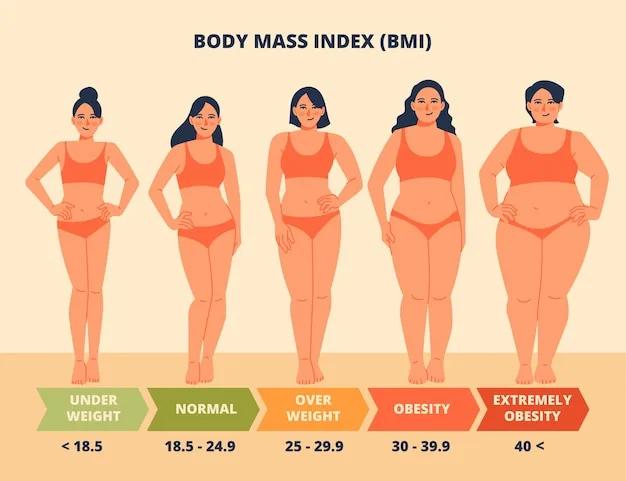
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely used measure to assess the weight-for-height ratio and determine whether an individual falls into the categories of underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. While maintaining a healthy BMI is essential for overall well-being, both underweight and overweight individuals face significant health risks. In this article, we will explore the consequences of an imbalanced BMI, shedding light on the potential dangers of being underweight or overweight.
Understanding BMI
Before delving into the health risks, it’s crucial to understand how BMI is calculated. BMI is obtained by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters. For adults, the World Health Organization (WHO) defines overweight as a BMI greater than or equal to 25, while obesity is classified as a BMI greater than or equal to 30. In children, BMI-for-age percentiles are used to determine weight status.
The health risks of being underweight
Nutritional deficiencies and delayed wound healing
One of the primary concerns associated with being underweight is the greater risk of nutritional deficiencies and malnutrition. Inadequate nutrient intake can lead to a range of health problems, including weakened immune function, impaired wound healing, and hormonal abnormalities. Essential vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin D, iron, and calcium, are often lacking in the diets of underweight individuals, compromising their overall health and well-being.
Increased susceptibility to infections
Being underweight weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections. A compromised immune response can result in frequent bouts of illness, longer recovery periods, and an increased risk of developing severe complications from common infections. This vulnerability to infections further highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy weight.
Risk of chronic diseases: Osteoporosis and others
Underweight individuals are at a higher risk of developing chronic health conditions such as osteoporosis. Insufficient weight-bearing exercise and inadequate nutrient intake contribute to reduced bone density and increased susceptibility to fractures. Hormonal imbalances associated with being underweight can further exacerbate the risk of osteoporosis.
Additionally, studies have shown that underweight individuals may face an increased risk of other chronic diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. The underlying mechanisms linking being underweight to these diseases are complex and multifactorial, involving metabolic dysregulation, hormonal imbalances, and inflammatory processes.
The health risks of being overweight
Type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance
One of the most significant health risks associated with being overweight is the development of type 2 diabetes. Excess body weight contributes to insulin resistance, a condition in which the body’s cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin. This leads to elevated blood glucose levels and can eventually result in the onset of diabetes. Diabetes, if left unmanaged, can lead to a range of complications, including cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
High blood pressure and cardiovascular disease
Being overweight or obese significantly increases the risk of high blood pressure, also known as hypertension. Hypertension is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases such as heart disease and stroke. The excess weight places additional strain on the heart, leading to increased blood pressure and the potential for damage to blood vessels. Over time, this can result in the development of atherosclerosis, heart attacks, and other cardiovascular complications.
Sleep apnea and respiratory disorders
Obesity is closely linked to sleep apnea, a condition characterized by interruptions in breathing during sleep. Excess body fat, particularly around the neck and throat, can obstruct the airways and lead to disrupted breathing patterns. Sleep apnea not only affects the quality of sleep but also increases the risk of cardiovascular problems, daytime fatigue, and other respiratory disorders.
Metabolic syndrome and its consequences
Metabolic syndrome refers to a cluster of conditions that often coexist and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. These conditions include high blood pressure, high blood sugar, abnormal cholesterol levels, and excessive abdominal fat (waist circumference). The prevalence of metabolic syndrome is significantly higher among overweight and obese individuals, emphasizing the importance of weight management in reducing the risk of these interconnected health problems.
Increased risk of cancer
Numerous studies have established a strong association between excess weight and various types of cancer. Obesity increases the risk of developing cancers such as endometrial and breast cancer (particularly in postmenopausal women), ovarian, prostate, liver, gallbladder, kidney, and colon cancer. The underlying mechanisms linking obesity to cancer are complex and multifaceted, involving hormonal imbalances, chronic inflammation, and altered immune responses.
Childhood obesity and its long-term impact
Childhood obesity is a significant public health concern, with long-term implications for an individual’s health and well-being. Obese children are more likely to become obese adults, facing an increased risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and musculoskeletal disorders. Additionally, childhood obesity can negatively impact psychological well-being, self-esteem, and social relationships, leading to psychosocial difficulties.
Treating and managing weight-related health risks
The treatment and management of weight-related health risks require a multifaceted approach, involving lifestyle modifications, dietary interventions, regular physical activity, and, in some cases, medical interventions. A comprehensive treatment plan should be tailored to the individual’s specific needs, addressing underlying causes, promoting healthy weight loss or gain, and providing necessary support for sustainable behavioral changes.
Lifestyle modifications and dietary interventions to prevent weight gain
For individuals who are overweight or obese, healthy lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in weight management. Adequate amounts of protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats should be incorporated into one’s diet. This includes adopting a balanced nutritious healthy eating diet that emphasizes whole foods, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Portion control, mindful eating, and avoiding processed and sugary foods are essential for sustainable weight loss. Seeking guidance from a registered dietitian or nutritionist can provide personalized dietary recommendations and support.
Regular physical activity
Incorporating regular physical activity into daily routines is vital for maintaining a healthy weight and reducing the risk of weight-related health problems. Engaging in aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises can help burn calories, build muscle, improve cardiovascular health, and enhance overall well-being. It’s recommended to aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week.
Medical interventions
In certain cases, medical interventions may be necessary to address weight-related health risks. These interventions may include pharmacological treatments, weight-loss medications, and, in severe cases, bariatric surgery. Medical interventions should always be supervised by qualified healthcare professionals and considered when lifestyle modifications alone are insufficient to manage health risks.
Conclusion
Maintaining a balanced BMI is essential for overall health, well-being and quality of life. Both underweight and overweight individuals face significant risks of medical conditions, ranging from diabetes, heart disease, and cancer to hormonal imbalances, compromised immune function, and psychological difficulties. By understanding the consequences of an imbalanced BMI, individuals can take proactive steps towards achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through lifestyle modifications, a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and, when necessary, medical guidance. Remember, prioritizing and investing in your health today can lead to a healthier and more fulfilling future.
Sources
- Health Risk and Underweight – PMC
- Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity – Healthy Weight, Nutrition, and Physical Activity – CDC
- Obesity – WHO
- Obesity and overweight – WHO
Medical Disclaimer
NowPatient has taken all reasonable steps to ensure that all material is factually accurate, complete, and current. However, the knowledge and experience of a qualified healthcare professional should always be sought after instead of using the information on this page. Before taking any drug, you should always speak to your doctor or another qualified healthcare provider.
The information provided here about medications is subject to change and is not meant to include all uses, precautions, warnings, directions, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or negative effects. The absence of warnings or other information for a particular medication does not imply that the medication or medication combination is appropriate for all patients or for all possible purposes.