Fungal Infections
Get valuable insights into Fungal Infections, including its causes, symptoms, prevention strategies, and treatment options, while also learning about how you can lower the cost of the medications used to treat Fungal Infections.

MEDICAL INFORMATION
Fungal Infections Key Facts
Related Medications
Fungal infections, are infectious diseases caused by various types of fungi, can affect different parts of the body and cause a wide range of symptoms. Fungi are present in the environment and can thrive in certain conditions, leading to infections in susceptible individuals. Understanding the causes, types, symptoms, and treatment options for fungal infections is crucial for accurate diagnosis, effective management, and prevention of complications. Here, we provide you with an overview of fungal infections, shedding light on their diverse nature and the importance of prompt intervention.
What are the causes of fungal infections?
Fungal diseases are caused by various types of fungi, which are present in the environment. These fungi can infect humans when they come into contact with the skin, nails, or mucous membranes, leading to an overgrowth and subsequent infection. The causes of fungal infections can vary depending on the specific type of infection, but here are some common causes
Fungal Exposure
Fungi are abundant in the environment and can be found in soil, plants, animals, and even the air we breathe. Direct contact with fungal spores or elements can lead to infection. For example, walking barefoot on contaminated soil can cause athlete’s foot or coming into contact with infected animals can lead to ringworm
Weakened Immune System
A weakened immune system can make individuals more susceptible to fungal infections. Conditions such as HIV/AIDS, diabetes, cancer, organ transplantation, or the use of immunosuppressive medications can compromise the body’s ability to fight off fungal infections, allowing the fungi to thrive and cause infection
Warm and Humid Environments
Fungi thrive in warm and moist environments. Areas of the body that are often warm and moist, such as the groin, armpits, or spaces between toes, provide an ideal breeding ground for fungal growth. Prolonged exposure to damp environments, such as wearing sweaty shoes or wet clothing, can increase the risk of fungal infections
Poor Hygiene
Inadequate personal hygiene practices can contribute to the development of fungal infections. Failure to regularly clean and dry the skin, especially in areas prone to moisture or friction, can create an environment conducive to fungal growth. Sharing personal items like towels, socks, or footwear can also spread fungal infections
Use of Antibiotics or Steroids
Certain medications, such as broad-spectrum antibiotics or long-term use of corticosteroids (such as in Asthma Inhalers), can disrupt the natural balance of microorganisms on the skin and mucous membranes. This imbalance can favor the overgrowth of fungi and increase the risk of developing fungal infections
Pre-existing Skin Conditions
Certain pre-existing skin conditions, such as eczema, psoriasis, or intertrigo (skin folds rubbing against each other), can create skin vulnerabilities and provide an entry point for fungal infections
What are the different types of fungal infections?
Fungal infections can affect various parts of the body, leading to different types of infections.
Superficial fungal infections
- Athlete’s foot (Tinea Pedis): This infection affects the feet, particularly the spaces between the toes, causing itching, redness, scaling, and sometimes blisters
- Jock itch (Tinea Cruris): This is a fungal skin infection that primarily affects the groin area, jock itch causes a red, itchy rash with a well-defined border
- Ringworm (Tinea Corporis): Ringworm can occur on various parts of the body, such as the scalp, body, or feet, causing a circular rash with red, scaly edges
Oral and oesophageal fungal infections:
- Oral thrush (candidiasis): This infection is characterized by the presence of white patches or plaques on the tongue, inner cheeks, and other areas of the mouth
- Oesophageal candidiasis: A fungal infection that affects the lining of the oesophagus, causing pain or difficulty swallowing
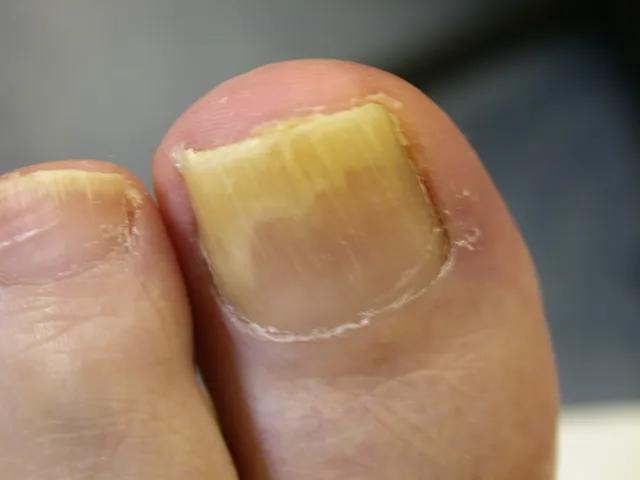
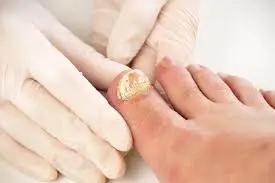
Nail fungal infections:
Onychomycosis: This type of infection affects the nails, often causing them to become thickened, discolored, brittle, and distorted
Cutaneous fungal infections:
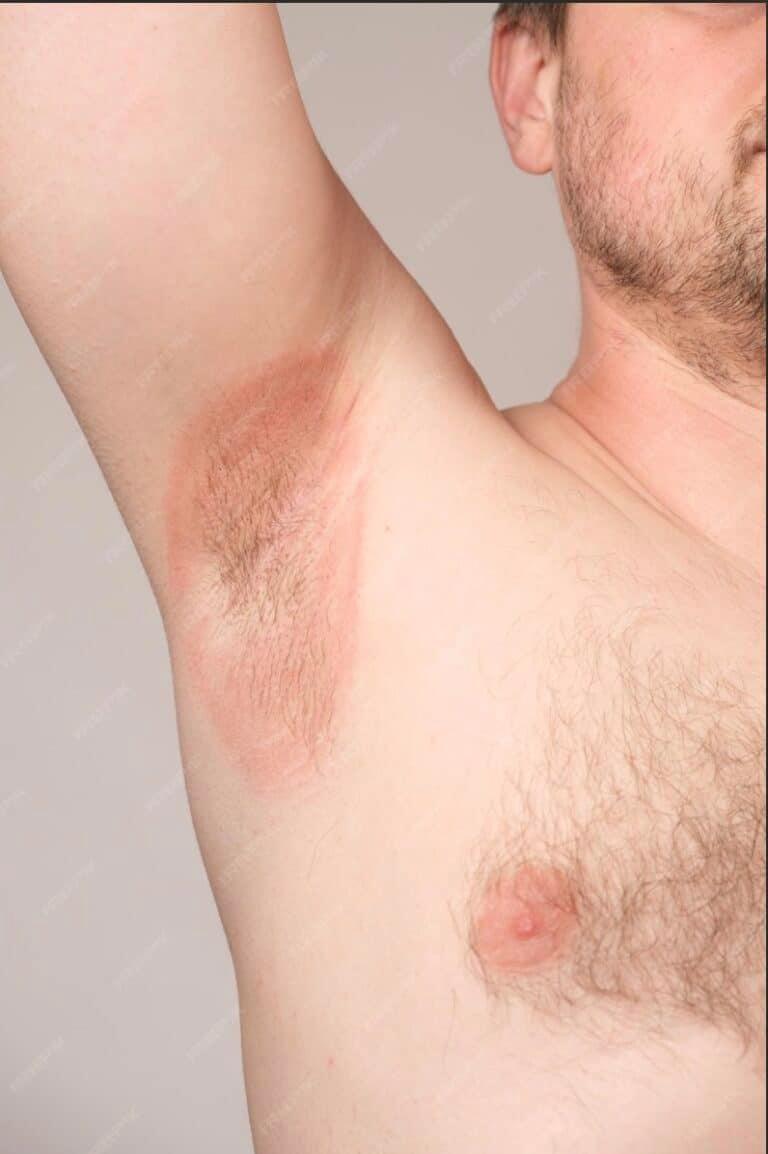
- Candidiasis: Candidiasis can occur in various areas of the body, such as the skin folds, genital area, or armpits, causing redness, itching, and irritation
- Tinea versicolor: This infection causes patches of discolored skin, typically lighter or darker than the surrounding skin, often on the chest, back, neck, or upper arms
Systemic fungal infections:
- Invasive candidiasis: A serious infection that can affect various organs and tissues, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems
- Aspergillosis: This infection primarily affects the lungs, but it can also spread to other organs in individuals with weakened immune systems or pre-existing lung conditions. If it spreads to the brain, heart or kidneys it can be life-threatening
- Cryptococcal meningitis: A fungal infection that affects the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, usually occurring in individuals with compromised immune systems
- Histoplasmosis: This is a systemic fungal infection that is caused by dimorphic fungus Histoplasma capsulatum which is found in bird and bat droppings. It mainly affects immunocompromised people
It is important to note that this list represents only a selection of common fungal infections, and there are many other types and subtypes of fungal infections that can occur. Proper diagnosis by a healthcare professional is necessary to identify the specific type of fungal infection and determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
What are the clinical symptoms of fungal infections?
The clinical symptoms of fungal infections can vary depending on the type of infection, the location on the body, and the individual’s immune response.
Skin Symptoms
- Redness and inflammation of the affected area
- Itching, burning, or stinging sensation
- Scaling or peeling of the skin
- Presence of a rash, blisters, or pustules
- Dry, cracked, or flaky skin
- Discoloration of the skin, such as darkening or lightening
Nail Symptoms
- Thickened nails
- Discolored nails, often yellow or brown
- Brittle or crumbly nails
- Distorted nail shape or texture
- Separation of the nail from the nail bed
- Build-up of debris under the nail
Oral Symptoms
- White patches or plaques on the tongue, inner cheeks, or other areas of the mouth (oral thrush)
- Redness and soreness of the mouth
- Difficulty swallowing or pain while eating
- Loss of taste or altered taste sensation
- Dry mouth or excessive saliva
Genital Symptoms
- Itching, redness, or soreness in the genital area
- Burning or discomfort during urination or sexual intercourse
- Abnormal vaginal discharge (in women)
- Balanitis (inflammation of the head of the penis) in men
Respiratory Symptoms
- Coughing, often accompanied by mucus or sputum production
- Shortness of breath or wheezing
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Flu-like symptoms, such as fever or chills
Systemic Symptoms
- Fever or elevated body temperature
- Fatigue, weakness, or general malaise
- Night sweats
- Weight loss
What are the treatment options for fungal infections?
The treatment options for fungal infections depend on the type, severity, and location of the infection, as well as the overall health of the individual. Fungal infections are typically treated with antifungal medications, which can be administered topically, orally, or intravenously.
Topical Antifungal
Creams, ointments, lotions, or powders containing antifungal agents can be applied directly to the affected area. They are commonly used for superficial infections, such as athlete’s foot, jock itch, or ringworm. Topical treatments are generally sufficient for mild to moderate infections
Oral Antifungal
In cases of more severe or widespread fungal infections, oral antifungal medications may be prescribed. These medications are taken by mouth and are capable of treating infections that affect deeper layers of the skin, nails, or mucous membranes. Oral antifungals are used for conditions like systemic candidiasis, severe cases of ringworm, or onychomycosis (nail fungal infections)
Intravenous Antifungal
For severe or systemic fungal infections, intravenous antifungal medications may be necessary. These medications are administered directly into the bloodstream through a vein and are typically reserved for serious infections, such as invasive candidiasis or certain types of fungal pneumonia
Combination Therapy
In some cases, a combination of topical, oral, or intravenous antifungal medications may be prescribed for more complex or resistant infections. This approach aims to maximize the effectiveness of treatment and improve outcomes
Duration of Treatment
The duration of antifungal treatment varies depending on the type and severity of the infection. Superficial infections may require a few weeks of treatment, while systemic infections or fungal nail infections may require several months of therapy. It is essential to complete the full course of treatment as prescribed, even if the symptoms improve, to ensure the complete eradication of the fungus and prevent recurrence
In addition to antifungal medications, certain preventive measures and self-care practices can help manage fungal infections and reduce the risk of recurrence. These may include keeping the affected area clean and dry, wearing breathable fabrics, avoiding sharing personal items, and practicing good hygiene.
What medications are used in the treatment of fungal infections?
The treatment of fungal infections involves the use of antifungal medications, which are specifically designed to target and eliminate fungal organisms. The choice of medication depends on the type and severity of the infection, the location of the infection, and the individual’s overall health.
Topical Antifungal Medications
- Clotrimazole: Available as creams, lotions, powders, or sprays, it is effective against a wide range of fungi and is commonly used for superficial fungal infections like athlete’s foot or vaginal yeast infections
- Miconazole: Found in various forms, including creams, powders, or suppositories, it treats superficial infections and is particularly effective against yeast infections
- Terbinafine: Often available as a cream or gel, it is effective against many types of fungi and is commonly used for ringworm, jock itch, or athlete’s foot
Oral Antifungal Medications
- Fluconazole: A widely used oral antifungal medication that treats a variety of fungal infections, including yeast infections, oral thrush, and systemic infections caused by Candida
- Itraconazole: Used for systemic fungal infections, including aspergillosis, blastomycosis, and fungal nail infections
- Ketoconazole: An oral antifungal agent used for various fungal infections, including systemic infections, and is sometimes used for its anti-androgenic effects in certain conditions like prostate cancer or hirsutism
- Griseofulvin: Effective against certain types of fungi, it is often used to treat fungal infections of the skin, hair, and nails, such as ringworm
Intravenous Antifungal Medications
- Amphotericin B: Administered intravenously, it is used for severe or systemic fungal infections, particularly those caused by Candida or Aspergillus
- Caspofungin: An intravenous medication used for invasive candidiasis, aspergillosis, and other serious fungal infections
It is important to note that these are just a few examples of commonly used antifungal medications. The specific medication and dosage prescribed will depend on factors such as the type of infection, the severity of the infection, the patient’s medical history, and any potential drug interactions.
What are the complications of fungal infections?
Fungal infections, if left untreated or not properly managed, can lead to various complications. The complications can vary depending on the type and severity of the fungal infection, the location of the infection, and the individual’s overall health. Here are some potential complications associated with fungal infections:
Spread of Infection
Fungal infections can spread to adjacent areas of the body, causing the infection to become more widespread or affecting different organ systems. For example, a fungal infection on the skin may spread to the nails or mucous membranes if not adequately treated
Chronic or Recurrent Infections
Some individuals may experience chronic or recurrent fungal infections, especially if the underlying cause or predisposing factors are not addressed. These persistent infections can significantly impact quality of life and require long-term management
Secondary Bacterial Infections
Fungal infections can weaken the skin or mucous membranes, making them more susceptible to secondary bacterial infections. Bacteria can colonize the compromised area, leading to additional symptoms and complications.
Disfigurement or Scarring
Certain fungal infections, such as severe cases of onychomycosis (nail fungal infection) or deep skin infections, can cause disfigurement of the affected area. This can lead to nail deformities, skin discolouration, or permanent scarring
Systemic Involvement
In individuals with weakened immune systems or systemic fungal infections, the fungus can enter the bloodstream and spread to other organs or body systems. This can lead to serious complications, such as fungal pneumonia, meningitis, or organ damage
Allergic Reactions
In some cases, individuals may develop allergic reactions to fungi or anti-fungal medications. These reactions can range from mild skin rashes to more severe symptoms, such as difficulty breathing or anaphylaxis
Psychological and Emotional Impact
Chronic or visible fungal infections, such as those affecting the skin or nails, can have a significant psychological and emotional impact on individuals. They may experience self-consciousness, decreased self-esteem, or social isolation
It’s important to seek timely medical care for fungal infections, especially if symptoms persist, worsen, or if there are signs of complications. Prompt and appropriate treatment can help prevent complications and promote healing.
What support organizations are available for people with fungal infections in the UK?
- The National Aspergillosis Centre (NAC) – The NAC is a UK center of expertise for the diagnosis and treatment of Aspergillosis, a type of fungal infection. They provide patient resources and information about the disease
- British Lung Foundation – They offer resources and support for lung conditions, including those caused by fungal infections such as aspergillosis
- British Skin Foundation – While not exclusively focused on fungal infections, they provide resources on skin health, including skin infections caused by fungus such as ringworm or athlete’s foot
- Fungal Infection Trust – The Fungal Infection Trust supports and promotes the education, research and patient care for fungal diseases
- Health Protection Scotland – They provide guidelines for the prevention and control of infections, including fungal infections
What support organizations are available for people with fungal infections in the US?
There are not many organizations specifically dedicated to supporting people with fungal infections in the United States, there are several broader health organizations that provide resources and support for infectious diseases, including fungal infections.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – The CDC provides extensive information about various types of fungal infections, including symptoms, prevention, and treatment
- National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) – NIAID conducts research and provides information on all types of infectious diseases, including fungal infections
- American Lung Association – While not solely focused on fungal infections, this organization provides resources and support for people with lung conditions, including those caused by fungal infections such as aspergillosis
- National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD) – NORD provides resources and support for people with rare diseases, including rare fungal infections
- American Academy of Dermatology – Provides resources and information related to skin infections, including those caused by fungus such as athlete’s foot, ringworm, and yeast infections
Summary
Fungal infections are common ailments caused by various types of fungi in the environment. Understanding their causes, types, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for accurate diagnosis, appropriate management, and prevention of complications. Practicing good hygiene, seeking timely medical care, and adhering to prescribed treatments are crucial in managing fungal infections effectively and promoting recovery.
Medical Disclaimer
NowPatient has taken all reasonable steps to ensure that all material is factually accurate, complete, and current. However, the knowledge and experience of a qualified healthcare professional should always be sought after instead of using the information on this page. Before taking any drug, you should always speak to your doctor or another qualified healthcare provider.
The information provided here about medications is subject to change and is not meant to include all uses, precautions, warnings, directions, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or negative effects. The absence of warnings or other information for a particular medication does not imply that the medication or medication combination is appropriate for all patients or for all possible purposes.