What You Need to Know About How Type 2 Diabetes Is Diagnosed

Type 2 diabetes is a prevalent chronic condition affecting millions of individuals worldwide. According to the American Diabetes Association, national health care costs attributable to diabetes in the U.S. have increased by $80 billion in the past 10 years from $227 billion in 2012 to $307 billion in 2022.
Diabetes occurs when the body’s cells do not respond normally to insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels. Understanding the diagnosis and management of type 2 diabetes is crucial for individuals living with the condition. This comprehensive guide provides valuable information on the symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, and effective strategies for managing type 2 diabetes.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
There are three main types of diabetes (also known as diabetes mellitus): type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes. It is characterized by insulin resistance, a condition in which the body’s cells fail to respond properly to insulin. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels. When cells become insulin-resistant, the pancreas compensates by producing more insulin. Over time, the pancreas may become unable to keep up with the body’s demand for insulin, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels.
Recognizing Symptoms and Risk Factors
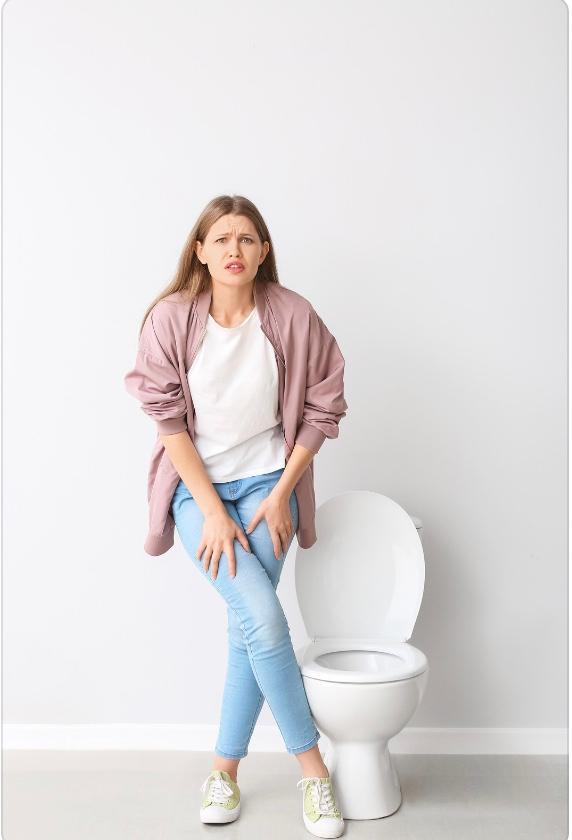
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes can develop gradually and may go unnoticed for an extended period. Common symptoms include frequent urination, excessive thirst, increased hunger, fatigue, blurry vision, slow-healing wounds, and numbness or tingling in the hands and feet. However, some individuals may not experience any noticeable symptoms.
Several risk factors contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. These include age, obesity or excess weight, sedentary lifestyle, family history of diabetes, high blood pressure, abnormal cholesterol levels, and ethnic backgrounds (Asian-American, African-American, Latino, Hispanic, Native American, Pacific Islander are higher risk groups). It is important to be aware of these risk factors and seek medical attention if necessary.
Diagnosing Type 2 Diabetes
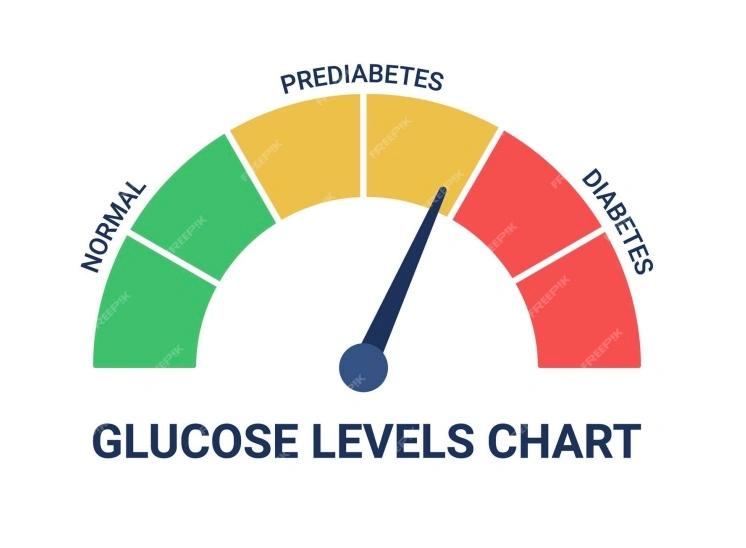
Diagnosing type 2 diabetes involves various tests conducted by healthcare professionals. One commonly used test is the A1C test, which measures average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. Results above 6.5% indicate diabetes. Other tests, such as the fasting plasma glucose test and the oral glucose tolerance test, can also help diagnose diabetes or prediabetes.
It is essential to consult a healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and to rule out other potential causes of symptoms. Early detection of type 2 diabetes allows for timely intervention and reduces the risk of complications.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Managing type 2 diabetes primarily involves making significant lifestyle changes. These changes include adopting a healthy eating plan, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight. A registered dietitian can provide personalized recommendations and guidance on creating a balanced meal plan that includes lean proteins, non-starchy vegetables, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates.
Regular exercise is crucial for managing blood sugar levels, achieving weight loss and preventing health problems. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, along with strength training exercises. Consult with a healthcare provider before starting any exercise program, especially if taking insulin or other medications.
Medication Options for Type 2 Diabetes
In some cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be enough to manage type 2 diabetes effectively. Healthcare providers may prescribe oral diabetes medications or injectable medications to help regulate blood sugar levels. Metformin is a commonly prescribed oral medication that improves insulin sensitivity and reduces glucose production in the liver.
Other medications, such as GLP-1 agonists and insulin, may be recommended based on individual needs. It is important to follow the prescribed medication regimen and discuss any concerns or side effects with a healthcare provider.
Blood Sugar Monitoring and Management
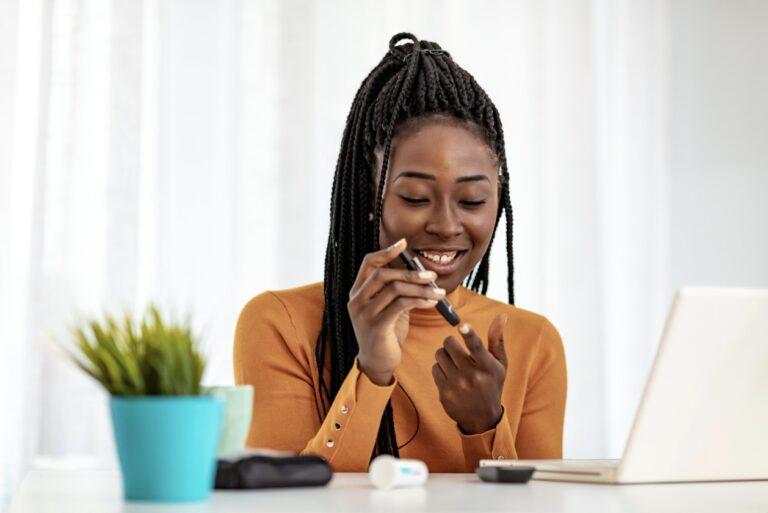
Regular blood sugar monitoring is a crucial aspect of managing type 2 diabetes. Monitoring helps individuals understand how their treatment plan is working and enables adjustments to medication, diet, and physical activity as needed. Blood sugar levels can be monitored using a glucose meter through fingerstick testing or through continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems.
Maintaining blood sugar levels within the target range recommended by healthcare providers helps prevent diabetes complications. Having chronically high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves throughout the body, causing a variety of serious health problems such as heart disease, kidney disease, retinopathy, nerve damage and foot problems (diabetic neuropathy) which may in severe cases lead to amputation. It is important to keep a record of blood sugar levels and share this information with the healthcare team for proper monitoring and management.
Stress Management and Emotional Well-being
Stress can affect blood sugar levels and make managing diabetes more challenging. Finding healthy ways to manage stress is essential for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Regular physical activity, getting enough sleep, practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation, and seeking support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends can all contribute to effective stress management.
Additionally, addressing emotional well-being is crucial when managing type 2 diabetes. It is normal to experience emotions such as frustration, stress, or sadness related to the condition. Seeking support from support groups or diabetes educators can provide valuable guidance and emotional support.
Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support
Diabetes self-management education (DSME) and support are essential components of effectively managing type 2 diabetes. DSME programs provide education on various aspects of diabetes management, including meal planning, blood sugar monitoring, medication management, and problem-solving skills.
Participating in DSME programs can enhance self-confidence, improve diabetes knowledge, and promote self-care behaviors. It is important to discuss with healthcare providers and seek recommendations for DSME programs available in the local community.
Type 2 Diabetes in Children and Teens
Type 2 diabetes is no longer limited to adults, as an increasing number of children and teens are being diagnosed with the condition. Childhood obesity and sedentary lifestyles contribute to the rising prevalence of type 2 diabetes in youth. Parents can play a crucial role in preventing or delaying type 2 diabetes in children by promoting healthy habits such as consuming less sugary drinks, increasing fruit and vegetable intake, and engaging in regular physical activity as a family.
Conclusion
Managing type 2 diabetes requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle changes, medication management, blood sugar monitoring, stress management, and support from healthcare professionals and loved ones. By adopting a healthy eating plan, engaging in regular physical activity, and adhering to medication regimens, individuals with type 2 diabetes can effectively manage the condition and reduce the risk of complications. Remember, effective management of type 2 diabetes is a lifelong commitment that can significantly improve overall health and well-being.
Sources
- Type 2 diabetes – Diagnosis and treatment – Mayo Clinic
- Diabetes Tests & Diagnosis – NIDDK
- Diagnosis – ADA
- Type 2 diabetes – Getting diagnosed – NHS
- $412.9 Billion in Health Care Dollars |ADA
NowPatient has taken all reasonable steps to ensure that all material is factually accurate, complete, and current. However, the knowledge and experience of a qualified healthcare professional should always be sought after instead of using the information on this page. Before taking any drug, you should always speak to your doctor or another qualified healthcare provider.
The information provided here about medications is subject to change and is not meant to include all uses, precautions, warnings, directions, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or negative effects. The absence of warnings or other information for a particular medication does not imply that the medication or medication combination is appropriate for all patients or for all possible purposes.