
Anticoagulants and Antiplatelet
Anticoagulants and antiplatelet medications are two classes of a common group called antithrombotic drugs. They are commonly referred to as ‘blood thinners’ and both work by preventing blood clots from forming. Antithrombotic drugs, which includes anticoagualant and antiplatelet drugs, are used in prevention and treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in high risk individuals , for the prevention and treatment of pulmonary embolism, and for the prevention of arterial embolism in patients with atrial fibrillation.
Below we dive deeper into the sub-classes of the two antithrombotic drugs and explore clinical uses, side effects and the mechanism of action.
What are Anticoagulants used for?
Anticoagulant drugs are used for the prevention and treatment of life-threatening conditions such as atrial fibrillation, venous thromboembolism, and valvular heart disease. They interfere with proteins in your blood, helping to prevent clots from forming (coagulation), that could otherwise lead to strokes, heart attacks, or other serious conditions.
What are Antiplatelet drugs used for?
Antiplatelet agents are also used for the management of thrombotic disorders in combination with anticoagulants. These include low dose aspirin, clopidogrel, prasugrel, ticlopidine and ticagrelor. They work by preventing blood cells such as platelets from sticking together, helping to reduce the formation of blood clots. This helps to prevent blood vessels from becoming blocked and the prevention of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks, angina, myocardial infarction, ischemic strokes, and peripheral vascular disease.
Types of Anticoagulant Drugs
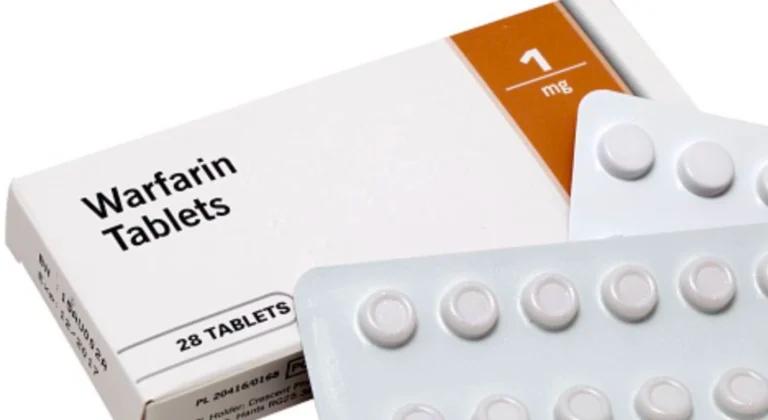
- Vitamin K antagonists such as warfarin (Coumadin)
- Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs) such as dabigatran, apixaban (Eliquis), and rivaroxaban
- Heparin and Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH)
Types of Antiplatelet Drugs
- Aspirin: Blocks enzymes that cause arterial clot formation
- ADP receptor inhibitors: Block ADP from attaching to platelets
- Glycoprotein IIB/IIIA inhibitors: Block receptors on platelets, preventing clot formation
- Phosphodiesterase inhibitors: Prevent platelet aggregation
- Protease-activated receptor (PAR-1) antagonists: Block platelet aggregation induced by thrombin
Dual anti-platelet therapy (DAPT) is often recommended for patients at high risk of cardiovascular problems to improve the prevention of clot formation. This is most beneficial in patients with acute coronary syndrome, where an in-stent thrombosis and cardiac event is high.
Managing risk factors and side effects associated with Anticoagulant therapy
The most common side effect when using anticoagulants is bleeding. Symptoms include unexplained bruising or bleeding gums. If you are taking warfarin, you will need regular blood tests to check your International Normalized Ratio (INR). These results will help your doctor decide if your medication is at the right dose for you.
Interactions with other medications you may be taking can also change the effectiveness of anticoagulants. These will also need to be monitored by your healthcare provider, to reduce the risks associated with blood clots.
Managing risks factors and side effects associated with Antiplatelet therapy
The most common risk associated with antiplatelets is the increased chance for bleeding events, with symptoms ranging from minor bruising to severe internal hemorrhages. Those taking antiplatelets may also experience longer bleeding times and so should always inform their healthcare provider about their treatment, to avoid interactions with other drugs.
Recent clinical trials have shown that dual therapy, consisting of oral anticoagulant therapy and a single antiplatelet agent, is a better treatment plan to reduce the risk of bleeding. Clinical guidelines also suggest dual therapy as a safer long-term approach than triple therapy when possible. Patients undergoing percutaneous coronary interventions or those with a history of venous thromboembolism will need a systematic review of their bleeding risks versus thrombotic risks.
Other treatment options include the use of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding in those patients taking more than one antithrombotic drug.
An individualized approach for patients ensures they receive the most suitable combination of medication based on their health status and needs to optimize their outcomes, while at the same time reducing the risk for potential complications.
Practical advice for patients taking Antithrombotics
Antithrombotic therapy requires consideration and compliance with prescribed treatment plans, especially in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) undergoing stenting. Guidelines to help manage this include:
- Taking your prescribed medications as recommended
- Having a consultation before adding new supplements or medications
- Discussing your diet, especially if you consume foods high in Vitamin K, which can affect blood thinning
- Carrying an emergency medical ID card with your medication plan and personal information. Also, ensuring your family members know about your condition and your treatment
Managing potential complications when being treated with Antithrombotics
If you have unusual bleeding, severe headaches and excessive bruising, you must get immediate medical attention. Also, you must not take aspirin with anticoagulants, unless told to do so by your doctor, as this may increase your risks for bleeding.
Tailored therapy based on individual risk
Guidelines recommend using dual therapy for most patients with atrial fibrillation or venous thromboembolism undergoing PCI, but moving to single therapy after 12 months, to reduce the risk of bleeding.
Sources
- Antiplatelet Drugs – Cleveland Clinic
- Anticoagulants and Antiplatelet Agents – Stroke
- BMJ
- Combined use of anticoagulant and antiplatelet on outcome after stroke in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation and systemic atherosclerosis – Nature
- Coronary artery disease patients requiring combined anticoagulant and antiplatelet therapy- Up To Date
- Circulation Research Online
NowPatient has taken all reasonable steps to ensure that all material is factually accurate, complete, and current. However, the knowledge and experience of a qualified healthcare professional should always be sought after instead of using the information on this page. Before taking any drug, you should always speak to your doctor or another qualified healthcare provider.
The information provided here about medications is subject to change and is not meant to include all uses, precautions, warnings, directions, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or negative effects. The absence of warnings or other information for a particular medication does not imply that the medication or medication combination is appropriate for all patients or for all possible purposes.