Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for overall well-being and plays a crucial role in preventing chronic diseases and health conditions. Research has consistently shown that people who are overweight or obese are at a higher risk of developing serious health issues compared to those with a healthy weight. Obesity has become one of the most important global public health issues. In this article, we will explore the link between body mass index (BMI) and overall health, discussing the potential risk factors and consequences associated with different BMI categories.
Understanding BMI
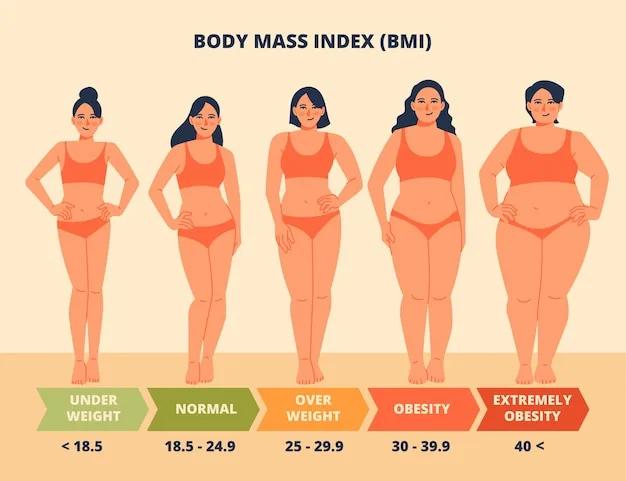
BMI, or body mass index, is a widely used measurement to assess an individual’s weight status. It is calculated by dividing a person’s body weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters. Based on the BMI value, individuals are categorized as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), a BMI of 18.5 or lower indicates underweight, while a BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 is considered normal weight. Overweight is defined as a BMI between 25 and 29.9, and obesity is classified as a BMI of 30 or higher.
It is important to note that BMI is a screening tool and does not directly measure body fat percentage or distribution. However, it provides a general indication of weight status and can be a useful starting point for understanding potential health risks. Some researchers argue your waist circumference and body fat distribution are better predictors of health risks than your BMI.
BMI may not accurately reflect weight status in certain populations, such as older adults, adolescents and individuals with different ethnicities. The relationship between BMI and health outcomes may vary across these groups. Asians for example, have more body fat at any given BMI compared to people of European descent. Therefore, the cut-offs for overweight and obesity may need to be lower for these populations. This is because an increased risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease begins at a BMI as low as 23kg/m2 in Asian populations. Some populations have equivalent disease risks at a higher BMI. It also does not work for use with children or adolescents who are still growing because their body composition changes throughout this period.
The impact of overweight and obesity on health
Increased risk of chronic conditions
Numerous studies have highlighted the association between being overweight and obesity and the increased risk of developing chronic conditions. One of the most significant risks is the development of high blood pressure or hypertension. Research has shown that excess weight puts additional strain on the heart, leading to elevated blood pressure levels. This, in turn, increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as coronary heart disease and stroke.
Being overweight or obese is a major contributor to dyslipidemia, a condition characterized by abnormal levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood. High LDL cholesterol, low HDL cholesterol, and elevated triglyceride levels are common in individuals with excess weight, further increasing the risk of heart disease.
Type 2 diabetes is another condition closely associated with obesity. Particularly central adiposity is the dominant risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes. The excess fat tissue in the body can cause insulin resistance, leading to high glucose levels and eventually the development of diabetes. Obesity also increases the risk of developing gallbladder disease, osteoarthritis, sleep apnea, and breathing problems.
Increased mortality risk
Research has consistently shown a higher mortality risk among individuals who are overweight or obese. A systematic evidence review conducted by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) found that being overweight and obesity are associated with an increased risk of all-cause mortality. The excess weight places a burden on various body systems, leading to a higher likelihood of premature death.
Association with cancer
Several studies have established a strong link between obesity and an increased risk of various types of cancer. The excess fat tissue in the body produces hormones and growth factors that can promote the growth of cancer cells. According to a population-based cohort study conducted in the UK, an elevated BMI is associated with a higher risk of 22 specific cancers, including breast, colorectal, and pancreatic cancer.
Impact on mental health
Obesity not only affects physical health but also has a significant impact on mental well-being. Research has shown a higher prevalence of mental illnesses such as clinical depression, anxiety, and other mental disorders among individuals with obesity. A three-decade prospective study conducted on women found a strong association between obesity and psychopathology. Another systematic review and meta-analysis confirmed the link between obesity and an increased risk of depression.
Decreased quality of life
Carrying excess weight can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Obesity and being overweight are associated with reduced physical functioning, increased body pain, and limitations in daily activities. These challenges can affect mobility, independence, and overall well-being. Moreover, the social and psychological implications of obesity, such as discrimination, isolation, and poor self-image, further diminish the quality of life. By maintaining a healthy weight, individuals can enhance their physical capabilities, improve mental well-being, and enjoy a higher quality of life.
Taking steps towards a healthy weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for reducing health problems and increasing well-being. If you are currently overweight or obese, there are interventions you can take to achieve a healthier weight and reduce the associated health risks. Here are some strategies to consider:
Balanced diet
Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet is essential for weight management. Focus on consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid or limit foods high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and excess calories. Portion control is also important to ensure you are consuming an appropriate amount of calories for your body’s needs to prevent weight gain.
Regular physical activity
Engaging in regular physical activity is key to achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with strength training exercises at least twice a week. Find activities you enjoy to make exercise a sustainable part of your lifestyle.
Seek professional guidance
If you are struggling with weight management, consider seeking guidance from healthcare professionals, such as registered dietitians or physicians specializing in obesity. They can provide personalized advice, develop a tailored nutrition and exercise plan, and offer support throughout your weight loss journey.
Set realistic goals
Setting realistic and achievable goals is crucial for long-term success. Instead of focusing solely on the number on the scale, aim to make sustainable lifestyle changes that promote overall health and well-being. Celebrate non-scale victories, such as improved energy levels, increased strength, and better overall mood.
Get support
Building a support system can greatly enhance your weight loss journey. Share your goals with friends and family members who can offer encouragement and accountability. Consider joining a support group or seeking online communities where you can connect with others facing similar challenges.
Conclusion
Maintaining a healthy weight is vital for overall health and reduces the risk of developing numerous chronic conditions and diseases. Being overweight and obese is associated with an increased risk of high blood pressure, dyslipidemia, type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease, stroke (called metabolic syndrome when someone has three or more of these diseases), cancer, mental health issues, and decreased quality of life. Taking steps towards achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet, regular physical activity, professional guidance, realistic goal-setting, and support can significantly improve overall well-being. Prioritize your health and make the necessary changes to live a healthier and happier life.
Sources
- NHLBI. 2013. Managing Overweight and Obesity in Adults: Systematic Evidence Review from the Obesity Expert Panel.
- Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults.
- Bhaskaran K, et al. Body-mass index and risk of 22 specific cancers: a population-based cohort study of 5.24 million UK adults. Lancet. 2014 Aug 30;384(9945):755-65.
- Kasen S, et al. Obesity and psychopathology in women: a three-decade prospective study. International Journal of Obesity. 2008;32(3):558-566.
- Luppino FS, et al. Overweight, obesity, and depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Archives of General Psychiatry. 2010;67(3):220-229.
- Roberts RE, et al. Prospective association between obesity and depression: evidence from the Alameda County Study. International Journal of Obesity. 2003;27(4):514-521.
- Association between Body Mass Index and Health-Related Quality of Life: The “Obesity Paradox” in 21,218 Adults of the Chinese General Population – PMC
- Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity – Healthy Weight, Nutrition, and Physical Activity – CDC
NowPatient has taken all reasonable steps to ensure that all material is factually accurate, complete, and current. However, the knowledge and experience of a qualified healthcare professional should always be sought after instead of using the information on this page. Before taking any drug, you should always speak to your doctor or another qualified healthcare provider.
The information provided here about medications is subject to change and is not meant to include all uses, precautions, warnings, directions, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or negative effects. The absence of warnings or other information for a particular medication does not imply that the medication or medication combination is appropriate for all patients or for all possible purposes.