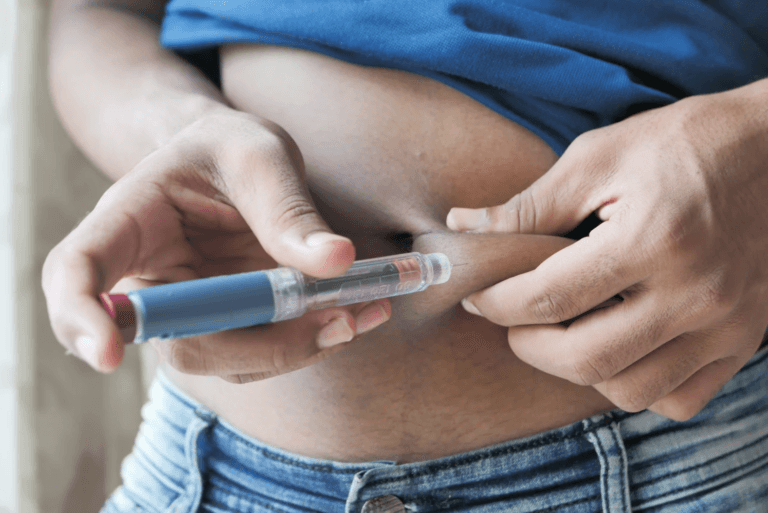
Insulin therapy is a vital component of diabetes management for many individuals. It helps regulate blood glucose levels and prevents complications associated with diabetes such as high blood pressure and coronary heart disease. However, like any medical treatment, insulin therapy has its pros and cons. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the benefits and risks of insulin therapy, providing valuable insights for diabetic patients considering or currently undergoing this treatment. We will also address common misconceptions and explore alternative treatment options for type 2 diabetes mellitus. So let’s dive in and uncover the truth about insulin therapy.
Understanding insulin and its role in diabetes management
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels. It allows cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream and use it for energy. In individuals with diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin (type 1 diabetes) or doesn’t effectively use the insulin it produces (type 2 diabetes). Insulin therapy is necessary to supplement the body’s insulin supply and maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
The benefits of insulin therapy
Insulin therapy offers several benefits for individuals with diabetes:
- Blood Sugar Control: Insulin helps regulate blood sugar levels, preventing them from becoming too high (hyperglycemia) or too low (hypoglycemia). Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and reduces the risk of complications
- Prevention of Diabetes Complications: Proper blood sugar control with insulin therapy can significantly reduce the risk of long-term complications associated with diabetes. These complications include heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems
- Flexibility in Dosage: Insulin therapy provides flexibility in dosage and can be tailored to an individual’s specific needs. Different types of insulin are available, each with its own onset and duration of action. This allows for personalized treatment plans that align with an individual’s lifestyle and blood sugar management goals
- Improved Quality of Life: By effectively managing blood sugar levels, insulin therapy can enhance overall wellness and quality of life. Stable blood sugar levels reduce symptoms such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision
The risks and challenges of insulin therapy
While insulin therapy offers significant benefits, it also comes with potential risks and challenges:
- Hypoglycemia: One of the main risks of insulin therapy is hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar. Taking too much insulin or not consuming enough carbohydrates can cause blood sugar levels to drop too low. Hypoglycemia can lead to symptoms such as dizziness, confusion, sweating, and even loss of consciousness if left untreated
- Weight gain: Some individuals may experience weight gain when starting insulin therapy. Insulin promotes the storage of glucose and can lead to increased fat deposition. However, with proper diet and exercise, weight gain can be managed and minimized
- Injection site reactions: Insulin is typically administered through injections, which can sometimes cause discomfort or localized reactions at the injection site, such as redness, swelling, or itching. Rotating injection sites and using proper injection techniques can help minimize these reactions
- Treatment adherence: Insulin therapy requires strict adherence to treatment plans, including proper timing and dosage. Failing to adhere to the prescribed insulin regimen can result in uncontrolled blood sugar levels and an increased risk of complications
- Fear of needles: Some individuals may experience anxiety or fear related to injecting insulin. This can make it challenging to consistently and effectively administer insulin. Alternative delivery methods, such as insulin pens or pumps, may be considered to alleviate needle-related anxiety
When is insulin therapy recommended?
Insulin therapy is recommended in various situations for individuals with diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes: Individuals with type 1 diabetes, where the pancreas doesn’t produce insulin, require lifelong insulin therapy. Insulin is necessary for survival in these cases
- Type 2 diabetes: For individuals with type 2 diabetes, insulin therapy may be necessary if other treatment options, such as oral medications and lifestyle changes, fail to adequately control blood sugar levels. In this type of diabetes, the body is insulin-resistant or produces too little insulin. Insulin therapy can be initiated early in the course of diabetes or added to the treatment plan as the disease progresses
- Gestational diabetes: Pregnant individuals with gestational diabetes may require insulin therapy if blood sugar levels cannot be managed through diet and exercise alone. Insulin therapy during pregnancy aims to maintain stable blood sugar levels to protect the health of both the mother and the baby
- Temporary needs: Insulin therapy may be required for temporary periods, such as during surgery while taking certain medications (e.g., steroids), or in cases of diabetic ketoacidosis (a life-threatening condition characterized by high blood sugar and ketone buildup)
It’s important to note that insulin therapy should always be prescribed and monitored by a healthcare professional. They will determine the appropriate insulin regimen based on an individual’s specific needs, blood sugar levels, and lifestyle factors.
Types of insulin and their characteristics
Insulin therapy encompasses various types of insulin, each with its own characteristics and uses. These include rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, long-acting, and premixed insulins. Let’s explore each type in more detail:
Rapid-acting insulin
Rapid-acting insulin, also known as mealtime insulin, is designed to quickly lower blood sugar levels after meals. It has a fast onset of action, typically within 15 minutes, and its effects peak within 1 to 2 hours. The duration of action is around 3 to 5 hours. This type of insulin works well when taken just before or immediately after meals to manage post-meal blood sugar spikes.
Short-acting insulin
Short-acting insulin, also known as regular insulin, takes slightly longer to start working compared to rapid-acting insulin, typically within 30 minutes. Its peak effects occur within 2 to 3 hours, and it lasts for approximately 5 to 8 hours. Short-acting insulin is usually taken 30 minutes before a meal to control blood sugar levels during and after eating.
Intermediate-acting insulin
Intermediate-acting insulin has a slower onset of action, usually within 1 to 3 hours. It peaks around 4 to 12 hours after administration and can last for 12 to 16 hours. This type of insulin provides a steady release of insulin throughout the day, helping to maintain stable blood sugar levels between meals and overnight. It is typically taken twice daily to provide basal, or background, insulin coverage.
Long-acting insulin
Long-acting insulin, also known as basal insulin, has a delayed onset of action, typically within 1 to 2 hours. It provides a slow and consistent release of insulin over an extended period, usually lasting around 20 to 26 hours. Long-acting insulin helps maintain a stable baseline level of insulin throughout the day and night, reducing the risk of high blood sugar levels when not eating. It is usually taken once daily.
Premixed insulin
Premixed insulin combines a rapid- or short-acting insulin with an intermediate-acting insulin in a fixed ratio. This type of insulin provides both basal and bolus coverage in a single injection. The ratio of rapid- or short-acting insulin to intermediate-acting insulin varies depending on the specific product. It is typically taken before meals to control post-meal blood sugar spikes.
The choice of insulin type and formulation depends on various factors, including an individual’s overall diabetes management plan, blood sugar control goals, and lifestyle considerations. A healthcare professional will work closely with the individual to determine the most appropriate insulin regimen.
Insulin delivery methods: Beyond injections
Insulin can be delivered through various methods, offering alternatives to traditional injections. These delivery methods include insulin pens, insulin pumps, and inhalers:
Insulin pens
Insulin pens are convenient and user-friendly devices that resemble writing pens. They are designed to administer insulin with ease and precision. Insulin pens come pre-filled with insulin cartridges or as reusable devices that require cartridge replacement. They provide a discreet and convenient way to administer insulin, allowing for precise dosage adjustments and minimizing the risk of dosing errors. Insulin pens are available for different types of insulin, offering flexibility in insulin therapy.
Insulin pumps
Insulin pumps are small devices that deliver a continuous supply of rapid-acting insulin throughout the day. The pump is connected to the body via a tiny tube inserted under the skin, usually in the abdomen. Insulin pumps provide both basal insulin (continuous background insulin) and bolus insulin (additional insulin taken before meals). The pump can be programmed to deliver precise doses of insulin based on an individual’s insulin needs. Insulin pumps offer greater flexibility in dosing and can be adjusted to accommodate changes in lifestyle and activity levels.
Inhalers
Inhaled insulin is a newer option for delivering insulin. It involves using an inhaler device to breathe in powdered insulin. Inhaled insulin is rapid-acting and is typically taken before meals to control post-meal blood sugar spikes. It offers an alternative to injections and can be particularly useful for individuals who have a fear of needles. However, it is important to note that inhaled insulin is not suitable for everyone and may not be recommended for individuals with certain respiratory conditions.
Managing insulin therapy: Tips for success
To ensure a safe and successful insulin therapy experience, it is important to follow these helpful tips:
- Work closely with your healthcare team: Diabetes management is a collaborative effort between individuals and their healthcare team. Regularly consult with your healthcare provider to discuss your insulin regimen, blood sugar monitoring, and any concerns or questions you may have
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly: Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial for adjusting insulin doses and maintaining optimal blood sugar control. Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for monitoring frequency and target ranges
- Follow a consistent meal plan: Consistency in meal timing and composition can help maintain stable blood sugar levels and optimize insulin therapy. Work with a registered dietitian or diabetes educator to develop a personalized meal plan that aligns with your insulin regimen
- Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity, regulate blood sugar levels and reduce obesity. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate exercise regimen for your specific needs and adjust your insulin doses accordingly
- Store insulin properly: Insulin should be stored according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Incorrect storage can affect insulin effectiveness. Avoid exposing insulin to extreme temperatures or direct sunlight
- Practice proper injection technique: If you administer insulin through injections, ensure that you are using the proper injection technique. Rotate injection sites and follow a consistent schedule to minimize discomfort and injection site reactions
- Be prepared for hypoglycemia: Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, can occur with insulin therapy. Carry a source of fast-acting carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets or juice, to treat low blood sugar episodes promptly
- Communicate any concerns or issues: If you experience any side effects or have concerns about your insulin therapy, do not hesitate to contact your healthcare provider. They can provide guidance, adjust your treatment plan if necessary, and address any questions or challenges you may encounter
Remember, insulin therapy is a personalized treatment approach, and what works for one individual may not work for another. Open communication with your healthcare provider is key to optimizing your insulin therapy and achieving the best possible outcomes.
Debunking insulin therapy myths
Misconceptions surrounding insulin therapy can lead to unnecessary fears and hesitation. Let’s debunk some common myths associated with insulin therapy:
- Insulin is a sign of failure: Needing insulin does not indicate failure or a lack of effort in managing diabetes. Insulin therapy is a crucial treatment option that can greatly improve blood sugar control and overall health. It is not a reflection of personal failure
- Insulin causes dependency: Insulin is a necessary hormone for individuals with type 1 diabetes and many with type 2 diabetes. It is not addictive, and its use is essential for managing blood sugar levels effectively
- Insulin leads to weight gain: While some individuals may experience weight gain when starting insulin therapy, it is not a universal effect. With proper diet and exercise, weight gain can be managed, and weight stabilization or even weight loss can be achieved
- Insulin injections are painful: Modern insulin delivery devices, such as insulin pens, have thin needles that cause minimal discomfort. Proper injection technique and using the right needle size can further reduce discomfort. Additionally, alternative delivery methods like insulin pumps or inhalers eliminate the need for injections altogether
- Insulin is only for severe cases of diabetes: Insulin therapy is not limited to severe cases of diabetes. It can be beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes who are unable to achieve blood sugar control with oral medications or other non-insulin treatment options. Insulin therapy is individualized based on an individual’s specific needs
It is important to separate fact from fiction when it comes to insulin therapy. By dispelling these myths, individuals can approach insulin therapy with a better understanding and more confidence in its benefits.
Exploring alternative treatment options
While insulin therapy is often necessary for individuals with diabetes, alternative treatment options exist for managing type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes. These options may be considered before or in conjunction with insulin therapy:
- Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can have a significant impact on blood sugar control. Regular physical activity, a balanced diet, weight management, and stress reduction techniques can all help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the need for insulin
- Oral medications: Several oral medications are available for managing type 2 diabetes. These medications work in various ways to lower blood sugar levels. They can be used alone or in combination with other medications, including insulin, to achieve optimal blood sugar control
- Non-insulin injectables: In addition to insulin, there are injectable medications called glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 agonists) that can enhance blood sugar control. These medications stimulate insulin production, reduce glucagon secretion, and slow down gastric emptying. GLP-1 agonists can be used as an alternative to or in combination with insulin therapy
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM): CGM systems allow individuals to monitor their blood sugar levels continuously. These devices provide real-time glucose readings, trends, and alerts, helping individuals make informed decisions about insulin therapy, diet, and physical activity
It is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for managing diabetes. Treatment decisions should be based on individual needs, blood sugar control goals, and considerations of lifestyle factors.
Conclusion
Insulin therapy plays a critical role in managing diabetes and maintaining stable blood sugar levels. While it has its risks and challenges, the benefits of insulin therapy, such as blood sugar control and prevention of complications, are substantial. Understanding the different types of insulin, delivery methods, and tips for success can help individuals navigate their insulin therapy journey with confidence. Additionally, debunking misconceptions and exploring alternative diabetes treatment options can provide a comprehensive perspective on managing the condition effectively. The best way to make a decision is to talk to your diabetes care team to figure out the best option for you.
NowPatient has taken all reasonable steps to ensure that all material is factually accurate, complete, and current. However, the knowledge and experience of a qualified healthcare professional should always be sought after instead of using the information on this page. Before taking any drug, you should always speak to your doctor or another qualified healthcare provider.
The information provided here about medications is subject to change and is not meant to include all uses, precautions, warnings, directions, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or negative effects. The absence of warnings or other information for a particular medication does not imply that the medication or medication combination is appropriate for all patients or for all possible purposes.