Arthritis is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by inflammation in the joints, resulting in pain, swelling, and stiffness. While there is no cure for arthritis, there are various treatment options available to manage arthritis pain and other symptoms. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different interventions for arthritis, including medications, physical therapy, and surgery.
Understanding arthritis
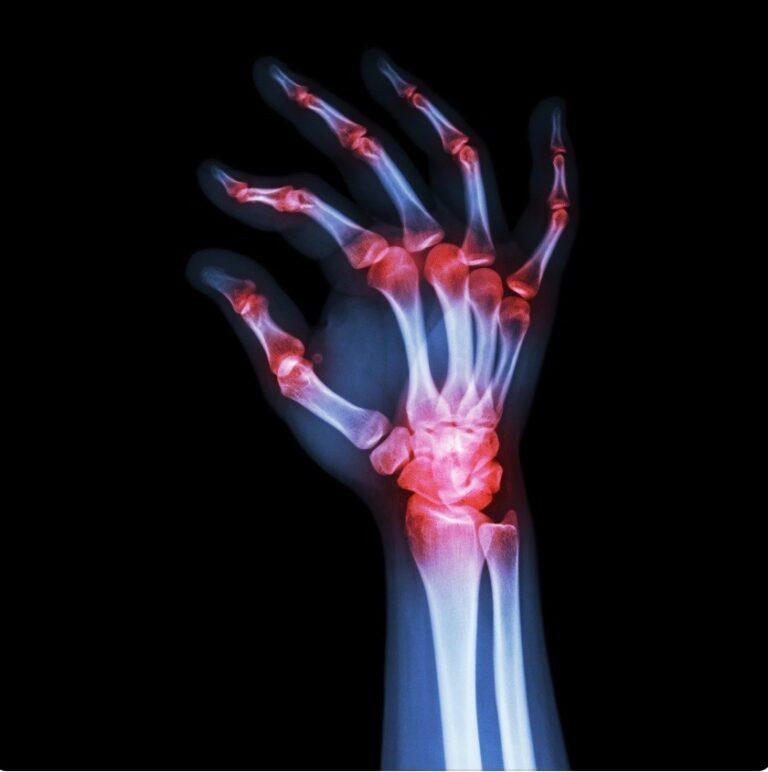
Arthritis is a complex disease that can affect individuals of all ages. It is not a single condition, but rather a term used to describe various types of joint inflammation. The most common forms of arthritis include rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA).
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation in the joints. It typically affects the small joints in the hands and feet and can progress to larger joints as the disease worsens. Osteoarthritis, on the other hand, is a degenerative joint disease that occurs when the cartilage between the joints wears down over time. It is commonly seen in weight-bearing joints such as the hips and knees.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing arthritis involves a combination of physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. During the physical exam, doctors will check for joint swelling, redness, and warmth. They will also assess the range of motion and mobility of the joints.
Laboratory tests, such as blood tests, can help identify the specific type of arthritis and rule out other conditions. These tests can measure markers of inflammation, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). In some cases, doctors may also analyze joint fluid obtained through a procedure called joint aspiration.
Imaging studies, including X-rays, CT scans, MRI, and ultrasound, can provide detailed images of the joints and help identify any structural abnormalities or damage. X-rays are commonly used to visualize bone and cartilage loss, while MRI and ultrasound can provide more detailed images of soft tissues and fluid-filled structures near the joints.
Medications
Medications are often used for pain management and to reduce inflammation. The specific medications prescribed will depend on the type and severity of arthritis.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation in arthritis. They work by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are responsible for pain and inflammation. Over-the-counter NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, can provide temporary relief. However, stronger NSAIDs may be prescribed by a doctor for more severe symptoms.
It is important to note that long-term use of NSAIDs can have side effects, including stomach irritation, ulcers, and an increased risk of heart attack or stroke. Therefore, it is essential to use NSAIDs as directed and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are a group of medications that can slow down the progression of arthritis and prevent joint damage. These drugs work by suppressing the immune system and reducing inflammation.
Methotrexate is one of the most commonly prescribed DMARDs for rheumatoid arthritis. It is a powerful medication that can help control inflammation and prevent joint destruction. Other DMARDs, such as hydroxychloroquine and sulfasalazine, may also be used depending on the individual’s specific condition.
DMARDs are often prescribed in combination with other medications to achieve optimal results. Regular monitoring of blood tests is necessary to ensure the medication’s effectiveness and detect any potential side effects.
Biologic therapies
Biologic therapies, also known as biologic DMARDs, are a newer class of medications that target specific components of the immune system involved in the inflammatory process. These medications are typically used for moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis that has not responded well to other treatments.
Biologics are administered either through injections or intravenous infusions. They can provide significant relief from symptoms and slow down joint damage. However, they do carry an increased risk of infections and other side effects. It is important to discuss the potential benefits and risks of biologic therapies with a healthcare professional.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids also known as steroids, such as prednisone, are powerful anti-inflammatory medications that can provide rapid relief from arthritis symptoms. These medications are often used for short-term management of flare-ups or to control severe inflammation. Corticosteroids can be taken orally, injected directly into the affected joint, or applied topically as a cream or ointment.
Long-term use of corticosteroids can have significant side effects, including weight gain, osteoporosis, diabetes, and increased susceptibility to infections. Therefore, they are typically used sparingly and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Physical therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the management of arthritis. It focuses on improving joint function, reducing pain, and increasing mobility. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program that includes stretching, strengthening, and range-of-motion exercises.
Physical therapy can also involve the use of assistive devices, such as braces, splints, or crutches, to support and protect the joints. Heat and cold therapy, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation may also be used to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
Engaging in regular physical therapy sessions and following the prescribed exercises can help improve joint flexibility, strengthen surrounding muscles, and enhance overall physical well-being.
Surgery
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat severe arthritis that has not responded to conservative treatments. The decision to undergo surgery will depend on the individual’s specific condition, the extent of joint damage, and the impact on daily activities and quality of life.
Common surgical procedures for arthritis treatment include:
Joint repair
Joint repair procedures aim to restore the damaged joint and improve its function. These procedures are often performed arthroscopically, using minimally invasive techniques. During joint repair, the surgeon may smooth or realign the joint surfaces, remove damaged tissue, or repair ligaments and tendons.
Joint replacement
Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, involves removing the damaged joint and replacing it with an artificial joint (prosthesis). The most common joints that are replaced are the hips and knees. Joint replacement surgery can significantly reduce pain and improve joint function, allowing individuals to resume their normal activities.
Joint fusion
Joint fusion, also known as arthrodesis, is a procedure that permanently fuses the ends of two bones in a joint. This eliminates the joint space and prevents movement. Joint fusion is typically performed on smaller joints, such as those in the wrist, ankle, or fingers, and is often recommended when joint replacement is not feasible or effective.
Lifestyle modifications
In addition to medical treatments, making certain lifestyle modifications can help manage arthritis symptoms and improve overall well-being. Here are some lifestyle changes that can be beneficial:
Weight management
In people with arthritis maintaining a healthy weight is essential, especially for those with weight-bearing joints involved. Excess weight and obesity stress the musculoskeletal system, leading to increased joint pain and discomfort. Weight loss can help reduce joint strain and improve mobility.
Regular exercise
Engaging in regular, low-impact physical activity can help strengthen muscles, improve joint flexibility, and reduce pain. Activities such as swimming, walking, and cycling are gentle on the joints while providing cardiovascular benefits. Swimming and water aerobics may be good choices because the buoyancy of the water reduces stress on weight-bearing joints. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist to design an exercise program that is safe and effective for your specific condition.
Heat and cold therapy
Applying heat or cold to the affected joints can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Heat therapy, such as using heating pads or warm towels, can relax muscles and improve blood circulation. Cold therapy, such as ice packs or cold compresses, can numb the area and reduce swelling. It is important to use these therapies appropriately and avoid excessive heat or cold that may cause burns or frostbite.
Assistive devices
Using assistive devices, such as canes, walkers, or braces, can help support the joints and improve mobility. These devices can reduce strain on the joints and provide stability while walking or performing daily activities. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist to determine the appropriate assistive devices for your specific needs.
Alternative therapies
In addition to conventional treatments, some individuals with arthritis may find relief from alternative therapies. It is important to note that the effectiveness of these therapies may vary, and they should be used in conjunction with medical treatments. Here are some alternative therapies that have shown promise in managing arthritis symptoms:
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is an ancient Chinese practice that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. It is believed to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes and promote pain relief. Some individuals with arthritis have reported improved pain and mobility after acupuncture sessions.
Massage therapy
Massage therapy involves the manipulation of soft tissues to improve blood circulation, reduce muscle tension, and promote relaxation. It can help alleviate pain and stiffness in the affected joints. It is important to seek a licensed and experienced massage therapist who specializes in treating individuals with arthritis.
Herbal supplements
Some herbal supplements, such as turmeric, ginger, and Boswellia, have anti-inflammatory properties and may provide relief from arthritis symptoms. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any herbal supplements to ensure safety and effectiveness, especially if you are taking other medications.
Mind-body techniques
Mind-body techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and guided imagery, can help reduce stress, promote relaxation, and improve overall well-being. These techniques can complement medical treatments and help manage pain and inflammation associated with arthritis.
Conclusion
Arthritis is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive treatment approach. Medications, physical therapy, and surgery play important roles in managing symptoms, reducing inflammation, and improving joint function. It is important to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses individual needs and goals. Additionally, making lifestyle modifications and exploring alternative therapies can further enhance the management of arthritis and improve quality of life.
A rheumatologist (arthritis specialist) will help you understand all of your options—their benefits and their risks. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatments or therapies to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Sources
- Arthritis – Diagnosis and treatment – Mayo Clinic
- Arthritis Treatment – Arthritis Foundation
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Treatment: Medications, Surgery, Therapy – WebMD
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Brief Overview of the Treatment – PMC
Medical Disclaimer
NowPatient has taken all reasonable steps to ensure that all material is factually accurate, complete, and current. However, the knowledge and experience of a qualified healthcare professional should always be sought after instead of using the information on this page. Before taking any drug, you should always speak to your doctor or another qualified healthcare provider.
The information provided here about medications is subject to change and is not meant to include all uses, precautions, warnings, directions, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or negative effects. The absence of warnings or other information for a particular medication does not imply that the medication or medication combination is appropriate for all patients or for all possible purposes.