September 17, 2025 (Current Version)
March 28, 2025
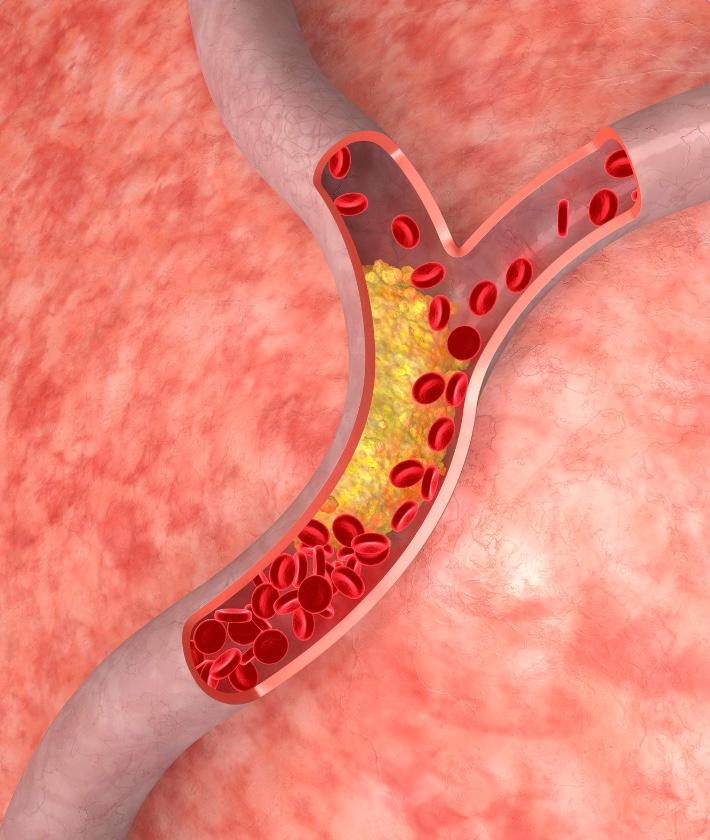
One of the most important risk factors for heart disease is high cholesterol. Cholesterol is a type of fat that circulates in the blood and it can build up on blood vessel walls, leading to narrowings and blockages called atherosclerosis. High cholesterol is a serious health problem. Luckily there are things you can do to reduce your blood cholesterol levels and improve your overall health. In this blog post we’ll give you some tips on how to cut down on cholesterol.
What is cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a fat-like substance that is found in all cells of the body. It helps to produce hormones, vitamin D, vitamin A and substances that help you digest food. Cholesterol also functions as part of the cell membrane. There are two main sources of cholesterol in your blood: cholesterol in the food you eat and cholesterol produced by your liver. Without getting too bogged down with the science let’s first take a look into what cholesterol is.
Many people know their cholesterol levels, but what they know is their total cholesterol level. Cholesterol circulates in the body in small packages called lipoproteins. These tiny round particles contain fat and protein. So how many kinds of fat particles (lipoproteins) are there and what are their functions?
- Chylomicrons – are the largest particles, but aren’t a concern regarding the hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis)
- Very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) particles – contain mainly triglycerides as the fat and are our main source of energy in the body. These are smaller than chylomicrons
- High-density lipoprotein (HDL) – also known as good cholesterol, the next smallest in size. HDL cholesterol functions to clean the arteries, helping to prevent coronary heart disease, peripheral arterial disease and strokes
- Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) – known as bad cholesterol. LDL cholesterol is the particle that carries cholesterol to the arteries. It is deposited here and its build-up causes the hardening of the arteries. This restricts blood flow and contributes to cardiovascular disease
Making lifestyle changes such as eating a heart-healthy diet and embracing healthy living habits such as exercising regularly is often the first step in treating high cholesterol.
Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fat that is found in oily fish, such as salmon, herring and mackerel. These fats are also found in flaxseed, chia seeds and walnuts. Omega-3 fatty acids have several health benefits, including the ability to lower cholesterol levels. LDL cholesterol is the “bad” cholesterol that can build up on the walls of arteries and lead to heart disease. Omega-3 fatty acids help to reduce the level of LDL cholesterol in the blood by inhibiting its production in the liver. In addition, omega-3 fats promote the excretion of cholesterol through the digestive system. As a result, foods high in omega-3 fatty acids can help to protect against heart disease.
Eat soluble fibre foods
Soluble fibre is a type of fibre that dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance. Soluble fibre is found in oats, barley, beans, lentils, peas and some fruits and vegetables. It is also available in powder form as a dietary supplement.
Soluble fibre binds to cholesterol in the intestine and prevents it from being absorbed into the bloodstream. This type of fibre can also reduce the amount of LDL cholesterol (bad cholesterol) in the blood by binding to it and removing it from the body. Soluble fibre also helps to regulate blood sugar levels by slowing down the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream. In addition, soluble fibre keeps you feeling full longer and can help with weight loss.
There are many different ways to lower cholesterol levels, but adding soluble fibre to your diet is a simple and effective way to do it. If you’re looking to lower your cholesterol, try incorporating some soluble fibre foods into your diet.
No trans fats
Trans fats are a type of fat that is created when liquid oils are turned into solid fats, such as margarine or shortening. Trans fats are often used in processed foods because they are cheaper than other types of fat and they help to extend the shelf life of products. Unfortunately, trans fats are also extremely unhealthy. They have been linked to heart disease, stroke and diabetes and they can increase levels of bad cholesterol while simultaneously lowering levels of good cholesterol. For these reasons, it is important to eliminate trans fats from our diet. Fortunately, this is becoming easier to do as food manufacturers are beginning to replace trans fats with healthier alternatives. Trans fats are sometimes listed on food labels as “partially hydrogenated vegetable oil”. By reading labels and being mindful of the ingredients in the foods we purchase, we can all make choices that will help to improve our health and reduce our risk of developing chronic diseases.
Less saturated fat
The main difference between saturated and unsaturated fats is the amount of saturated fatty acids present. Saturated fats have more saturated fatty acids, which means they are more likely to solidify at room temperature. Unsaturated fats have fewer saturated fatty acids, so they are more likely to remain liquid at room temperature. Both types of fat can be found in animal products and plants. Saturated fats are found in higher amounts in animal products, such as butter, lard, red meat and cream. Unsaturated fats are found in higher amounts in plant-based oils, such as olive oil and canola oil. Dietary guidelines recommend that people consume less saturated fat to lower their cholesterol levels. This is because saturated fat raises LDL cholesterol levels, which can lead to heart disease. When you consume less saturated fat, your LDL cholesterol levels will decrease over time. This can help to reduce your risk of developing heart disease.
Healthy living
Exercise regularly
Physical activity has numerous benefits for overall health, including reducing the risk of heart disease. One way that it does this is by lowering cholesterol levels. LDL or “bad” cholesterol can build up in the arteries and lead to heart attack or stroke. HDL or “good” cholesterol helps to remove LDL from the arteries and keep them clear. Regular physical activity helps to increase HDL levels and lower LDL levels, which reduces the risk of heart disease. In addition, physical activity can help to lower blood pressure and manage weight, both of which are also risk factors for heart disease. As a result, getting regular exercise is an important part of maintaining a healthy heart.
Quit smoking
Smoking cigarettes is well-known to be a major risk factor for heart disease. This is because smoking damages the lining of the arteries, making it more difficult for blood to flow smoothly. In addition, smoking increases LDL cholesterol levels and decreases HDL cholesterol levels. As a result, quitting smoking can have a profound impact on cholesterol levels. Within just a few weeks of quitting, LDL levels will start to drop and HDL levels will start to rise. In addition, the damage to the arteries will begin to heal, resulting in better blood flow and lower cholesterol levels over time. So if you’re looking to improve your cardiovascular health, quitting smoking is a great place to start. If you need help quitting, talk to your doctor about quitting aids such as nicotine gum or patches.
Lose weight if you are overweight or obese
High cholesterol levels are often associated with obesity, but even a moderate amount of weight loss can have a significant impact on cholesterol levels. Weight loss can also lower triglyceride levels, another type of fat that can contribute to heart disease. In addition to improving cholesterol levels, weight loss has many other benefits for heart health, including reducing high blood pressure and lowering the risk of diabetes. For these reasons, it is important for people who are trying to lower their cholesterol to focus on achieving a healthy weight. If you need help losing weight, talk to your healthcare professional about a weight-loss program that might be right for you.
Know your numbers
Get your blood lipid levels checked by your doctor at least once every five years starting at age 20 (earlier if you have a family history of heart disease). Knowing your numbers will help you determine if lifestyle changes or medication is needed to manage your cholesterol levels.
Healthy levels for different types of cholesterol as recommended by the NHS are:
- Total cholesterol – 5 or below mmol/L
- HDL (good cholesterol) – 1 or above mmol/L
- LDL (bad cholesterol) – 4 or below mmol/
- Fasting triglycerides (no food for several hours before the test) – 1.7 or below mmol/L
- Non-fasting triglycerides (when you eat as normal before the test) – 2.3 or below mmol/L
- Total cholesterol to HDL cholesterol ratio – 6 or below mmol/L
- These values may look confusing at first but your healthcare professional will explain the levels and your results
Top tips to cut down on cholesterol
Luckily, there are a number of simple food swaps that can help to lower cholesterol levels:
- Swap full-fat dairy products for low-fat varieties e.g. full-fat milk for skimmed milk
- Replacing butter and margarine with olive oil
- Avoid white bread, white rice, white pasta and white-flour foods like muffins, croissants, bagels, crackers, dried cereals, tortillas, pretzels and chips
- Eat whole grain foods such as wholegrain bread, brown rice, lentils, beans and chickpeas, oats and seeds
- Choosing leaner cuts of meat such as chicken or fish over fatty red meats
- Avoid coconut oil and palm oil and use olive oil instead
- Good sources of unsaturated fats are avocados, nuts and seeds
- Avoid buying baked goods, pre-packed snack foods and deep-fried foods
Making changes to your lifestyle is the first step in treating high cholesterol. This means healthy eating, exercising regularly and maintaining a healthy weight. If these lifestyle changes do not work, medication such as statins may be prescribed. Statins work by blocking the production of cholesterol in the liver. They are generally effective at reducing cholesterol levels, but they can have side effects such as muscle pain and fatigue. In addition, statins can interact with other medications, so it is important to discuss potential risks with your healthcare professional before starting any new medication.
Sources
- Six cholesterol-busting foods – Heart UK
- What is cholesterol? – Heart UK
- How to lower your cholesterol – NHS
- Cholesterol – CDC
Medical Disclaimer
NowPatient has taken all reasonable steps to ensure that all material is factually accurate, complete, and current. However, the knowledge and experience of a qualified healthcare professional should always be sought after instead of using the information on this page. Before taking any drug, you should always speak to your doctor or another qualified healthcare provider.
The information provided here about medications is subject to change and is not meant to include all uses, precautions, warnings, directions, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or negative effects. The absence of warnings or other information for a particular medication does not imply that the medication or medication combination is appropriate for all patients or for all possible purposes.