Genital Herpes Treatments
* Includes Free Private Prescription & Consultation.
† Applies to UK only.

START YOUR TREATMENT TODAY
Available Treatments for Genital Herpes
SAFE PRESCRIBING
Get Started With the Right Treatment for You
MEDICAL INFORMATION
Genital Herpes Key Facts

(Current Version)
Genital Herpes is a common STI (sexually transmitted infection) caused by the herpes simplex virus. The CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) reports over 40 million adults have Genital Herpes in the U.S.
Here, we will take a closer look at Genital Herpes, how it is transmitted, its symptoms, your treatment options, and how to prevent it.
Understanding Genital Herpes
Genital Herpes is classed as an STD (sexually transmitted disease). It is highly contagious and is caused by 2 types of the virus: (HSV-1) Herpes simplex virus type 1, which is associated with oral herpes (cold sores), and (HSV-2) Herpes simplex virus type 2, which is the primary cause of Genital Herpes.
Both types of the virus remain in your body even when you do not have any symptoms, and even though your immune system will usually keep the virus in check, it can be reactivated occasionally.
Transmission
The virus will enter your body through skin abrasions and mucous membranes, such as those in the nose, mouth, and genital area. Transmission occurs through direct physical contact with bodily fluids infected with the virus. These include vaginal fluids, saliva and semen. The virus is transmitted even when there are no symptoms of Genital Herpes.
Symptoms and outbreaks
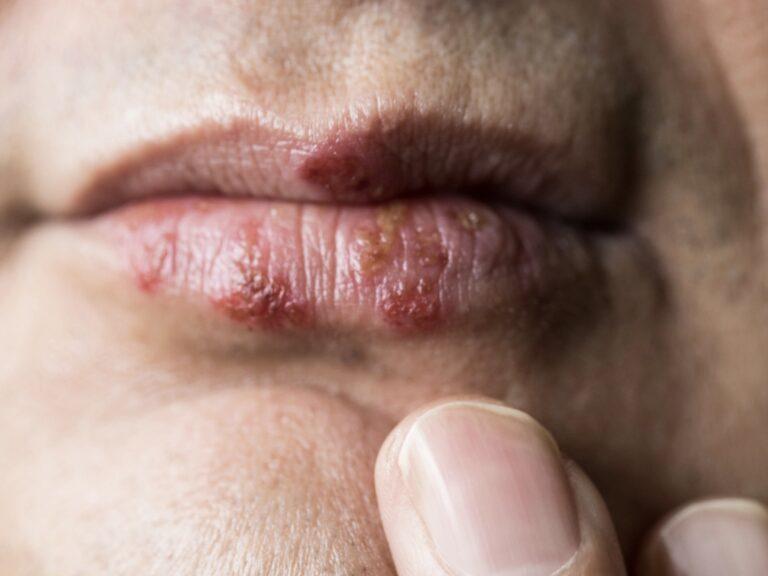
Symptoms will vary from person to person. While some may suffer with recurrent outbreaks, others may not experience any symptoms at all. Symptoms may include painful blisters, swelling, itching, or ulcers. Your first outbreak of Genital Herpes will occur within 2 to 12 days of being exposed to the virus. Your first episode of Genital Herpes will be more severe than any future outbreaks which will also not last as long as the first time.
Other symptoms of an outbreak, may include the formation of small blisters that erupt and form painful open sores, on or around the genitals, anus, thighs, buttocks, and mouth, pain when urinating, and flu-like symptoms such as a high temperature and body aches.
Many people with Genital Herpes mistake their symptoms for other conditions such as yeast infections, razor burns, or pimples. Some people may have very mild symptoms that are easily missed, making herpes more challenging to diagnose.
Diagnosis and testing
Diagnosis requires both a visual examination of the affected area and laboratory testing, using swabs taken from the sores or ulcers. Blood tests may also be taken to test for HSV antibodies, to check for past or current viral infections.
Testing for Genital Herpes may not be needed if symptoms are not present, but if you do have symptoms or think you have been exposed to the virus, you should seek a medical evaluation.
Managing Genital Herpes
There is no cure for Genital Herpes, but there are treatment options available to help manage your symptoms. These will help reduce the severity and how often outbreaks occur, as well as prevent the spread of the virus to sexual partners.
Treatment options
Antivirals are prescribed to help relieve Genital Herpes symptoms, speed up the healing process, and reduce the risk of transmission. Treatment is most effective at the first sign of an outbreak. Antiviral medicines include aciclovir, famciclovir, and valacyclovir.
How Genital Herpes is treated will vary depending on each individual and their circumstances. The two strategies are:
- Intermittent treatment, where the antiviral is taken when symptoms first appear or before symptoms develop fully. This will reduce the severity and how long symptoms persist
- Suppressive therapy, where the antiviral is taken daily to prevent further outbreaks. This type of treatment is recommended for those who have regular or severe outbreaks, to reduce their frequency and the risk of transmission
Alternative approaches and additional support
Some people may try alternative or complementary therapies to manage symptoms. However, there is limited evidence to support the effectiveness of alternative treatments.
Home care
Good hygiene and self-care can also help in the management of Genital Herpes. Keeping the affected area clean and dry, using mild cleansers, and cotton clothing can all help to reduce irritation. Ice packs or petroleum jelly to relieve any discomfort and practicing safe sex by using condoms, is also recommended.
Recurrences and triggers
Over time the severity and frequency of outbreaks tends to decrease and individuals may have long periods without any symptoms, but certain factors can trigger outbreaks. These include exposure to U.V. light, friction, illness, stress, and changes in hormone levels.
Pregnancy and Genital Herpes
Risk of complications for the baby are low if the infection was present before pregnancy, but there are precautions that should be taken to further reduce the risk, such as taking antivirals during pregnancy to manage symptoms and to reduce the risk of an outbreak during childbirth.
A cesarean section may be recommended if active Genital Herpes is present during childbirth to prevent transmission of the virus to the baby. Neonatal herpes can be life-threatening to a baby if exposed to the virus during childbirth.
Preventing the transmission of Genital Herpes
Preventing the transmission of Genital Herpes is crucial for individuals who are sexually active. Transmission can occur even when using barrier methods, such as condoms, however these tips can reduce the risk.
- Using barrier methods, such as condoms or dental dams, during sexual intercourse can reduce the risk of transmission. Condoms however, do not give 100% protection
- Having open and honest conversations with your partner are vital
- Daily use of antiviral medication can reduce the frequency of outbreaks and the risk of transmission
- Avoiding sexual contact and refraining from sexual activity during outbreaks will reduce the risk of transmission. But remember, herpes can still be spread when symptoms are not visible
- Regular testing for STIs, including Genital Herpes infections, is recommended for sexually active individuals. Early detection and treatment helps to prevent transmission
Living with Genital Herpes
Genital Herpes can be a challenge, physically and emotionally. Some tips for managing Genital Herpes include:
- Educating yourself about Genital Herpes and its management to reduce anxiety and promote self-care
- Discussing your diagnosis with trusted friends, family, or healthcare professionals. This can provide you with emotional support and help with feelings of embarrassment
- Exercising to help relieve stress
- Getting enough sleep, eating a healthy balanced diet, and good hygiene
- Joining support groups or online communities to share experiences and advice
Frequently asked questions
How is Genital Herpes transmitted?
Genital Herpes is transmitted through direct skin-to-skin contact or direct contact or exchange of bodily fluids during sex. This includes vaginal sex, anal sex, and oral sex. Herpes can be spread even when there are no symptoms or herpes sores present. Contrary to belief, herpes cannot be spread through contact with objects such as toilet seats or towels.
How do I know I have Genital Herpes?
Diagnosis requires both a visual examination of the affected area by a healthcare provider and laboratory testing. Blood tests may also be taken to test for antibodies, to check for past or current viral infections.
Conclusion
Genital Herpes is a common STI caused by the herpes simplex virus. There is no cure, but individuals can manage their conditions through medication, home care, and preventive measures.
If you think you have herpes or have concerns about your sexual health, speak to your doctor or a nurse for medical advice. Early diagnosis and treatment will help you manage your symptoms and reduce the risk of spreading the virus. Also, open communication with your sex partner and practising safe sex will help you deal with condition both physically and emotionally.
References
- NHS – Genital Herpes
- CDC – Genital Herpes
- Mayoclinic – Genital Herpes
- Hopkinsmedicine – Genital Herpes
- Betterhealth – Genital Herpes
NowPatient has taken all reasonable steps to ensure that all material is factually accurate, complete, and current. However, the knowledge and experience of a qualified healthcare professional should always be sought after instead of using the information on this page. Before taking any drug, you should always speak to your doctor or another qualified healthcare provider.
The information provided here about medications is subject to change and is not meant to include all uses, precautions, warnings, directions, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or negative effects. The absence of warnings or other information for a particular medication does not imply that the medication or medication combination is appropriate for all patients or for all possible purposes.
Related Articles
OUR CUSTOMERS VIEW
What Customers Love About Our Service
We want everyone to be happy and healthy, that’s what keeps us going. Read what some of them have to say about us.
Medicines Experts
Meet Our Medical Team
We are a broad skilled and passionate group of clinicians with experience of operating in health systems in the United Kingdom & United States. Providing excellent care and advice is at the heart of everything we do. You can read more about our medical team by visiting the medical team page or learn more about how we curate content by visiting our editorial process