Skin cysts or sebaceous cysts are common noncancerous bumps that can appear anywhere on the body. They are often harmless and rarely require treatment. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for skin cysts. Whether you have recently discovered a skin cyst or are simply curious about these benign growths, this article will provide you with the information you need to understand and manage them.
What are skin cysts?
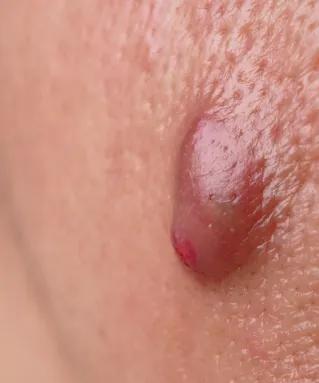
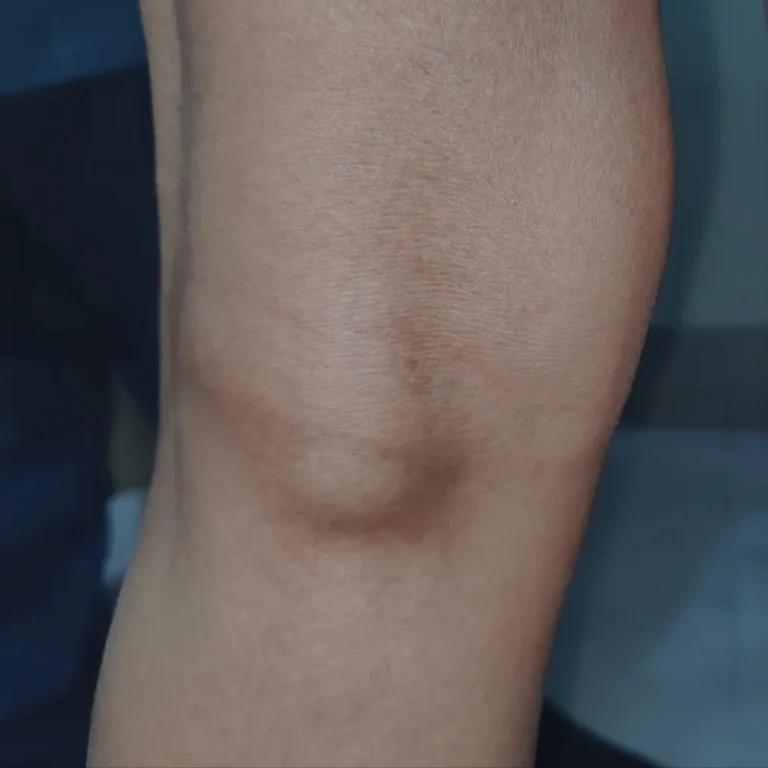
Skin cysts, also known as epidermoid cysts, are small bumps that develop beneath the skin’s surface. They are typically round and can vary in size from smaller than a pea to several centimetres across. Skin cysts are usually fluid-filled lumps or fluid-filled sacs and may have a small, dark spot in the centre. While they can occur on all parts of your body, they are most commonly found on the face, neck, trunk, and genital area.
Types of cysts
Skin cysts can manifest in various forms, depending on their location and underlying causes. Here are some of the most common types of skin cysts:
- Epidermoid cysts: These cysts develop in the top layer of the skin (epidermis) and are often filled with keratin. They are commonly found on the face, neck, and trunk
- Pilar cysts: Also known as trichilemmal cysts, pilar cysts form in hair follicles, usually on the scalp. They contain a substance called keratin, similar to epidermoid cysts
- Ganglion cysts: These cysts occur near joints or tendons, most commonly on the wrists, hands, and fingers. They are filled with a jelly-like fluid and are often associated with repetitive movements or joint stress
- Baker’s cysts: Baker’s cysts are fluid-filled swellings that develop at the back of the knee. They typically occur as a result of underlying knee joint conditions, such as arthritis or meniscal tears
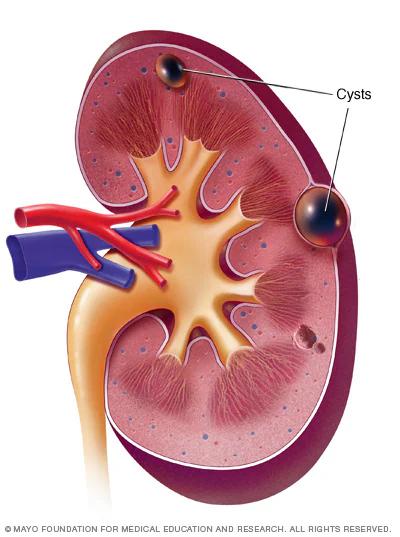
- Bartholin’s cysts: Bartholin’s gland cysts are small lumps or swellings that form on the opening of the vagina. They are caused by blockage or inflammation of the Bartholin’s glands, which are responsible for lubricating the vaginal area
- Meibomian cysts or chalazion: Small cysts or swellings on the eyelid, resulting from the blockage of the meibomian glands. They are often painless but can cause discomfort and blurred vision if they grow larger
- Pilonidal cysts form in the skin near the tailbone or lower back, and they sometimes contain ingrown hair
Causes of skin cysts
The exact cause of skin cysts is often unknown. However, they are believed to develop when the surface cells of the skin move deeper into the skin instead of shedding normally. These cells then multiply and form the walls of the cyst. The interior of the cyst is filled with a thick, yellow substance called keratin.
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing skin cysts. These include:
- Hair follicle or gland damage: Skin cysts can form when a hair follicle or oil gland in the skin becomes damaged or blocked, leading to the accumulation of keratin
- Rare genetic disorders: Certain rare genetic conditions, such as Gardner syndrome, can increase the risk of developing skin cysts
- Family history: Having a family member with a history of cysts, especially pilar cysts, may make an individual more susceptible to developing them
- Age and hormonal changes: Skin cysts are more common in adults, particularly middle-aged individuals. Hormonal changes during puberty and pregnancy can also contribute to their formation
- Skin irritation or injury: Skin cysts may develop in areas that experience repeated irritation or injury, such as scars, inflamed acne lesions, or previous surgical incisions
It is essential to note that skin cysts are not cancerous and cannot be transmitted from person to person.
Symptoms of skin cysts
Skin cysts usually do not cause any symptoms and are often painless. However, certain signs may indicate the presence of a skin cyst:
- Small, round bump: Skin cysts appear as raised bumps under the skin, typically on the face, neck, or trunk
- Blackhead: Some cysts may feature a tiny blackhead at the center, which is a result of debris accumulating in the cyst
- Drainage: In some cases, cysts may drain a thick, yellow, and occasionally foul-smelling material
- Inflammation and infection: If a cyst becomes infected or inflamed, it may appear red, swollen, and tender
When to seek medical attention
Most skin cysts do not require medical intervention and can be left untreated. However, there are situations where it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional:
- Rapid growth: If a cyst grows rapidly in size, it is recommended to seek medical advice
- Pain or infection: Cysts that become painful, ruptured, or infected should be evaluated by a healthcare provider
- Constant irritation: Cysts occurring in areas that are constantly irritated, such as the fingers or toes, should be examined
- Cosmetic concerns: If the appearance of a cyst bothers you, a doctor can discuss options for removal
Diagnosis of skin cysts
In most cases, a healthcare provider can diagnose a skin cyst through a physical examination. They will assess the appearance, size, and location of the cyst. In some instances, additional tests, such as imaging or a biopsy, may be required to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other conditions.
Treatment options for skin cysts
Skin cysts that are not causing any problems generally do not require treatment. However, if a cyst becomes infected, painful, or interferes with daily activities, treatment options may be considered. The available treatment approaches include:
- Antibiotics: In the case of an infected cyst, antibiotics may be prescribed to eliminate the infection
- Drainage: A healthcare professional may drain the fluid or pus from an infected cyst to relieve symptoms
- Surgical removal: Large, painful cysts that significantly impact daily life can be surgically removed. This procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia, and a small scar may result
- Cosmetic removal: If a cyst is located in a visible area of the body and causes cosmetic concerns, it can be removed for aesthetic reasons. However, cosmetic removal is often not covered by insurance and may require out-of-pocket expenses
Prevention and self-care
While it is not always possible to prevent the development of skin cysts, there are a few self-care measures that can help minimize the risk:
- Avoid squeezing or popping cysts: Manipulating a cyst can lead to infection or further complications
- Practice good hygiene: Keeping the skin clean and dry may reduce the likelihood of cysts becoming infected
- Protect the skin: If you are prone to cysts, taking precautions to protect your skin from injuries or irritants can be beneficial
Conclusion
Skin cysts are common benign growths that typically do not require treatment. They are slow-growing, painless, and often harmless. While cysts can be bothersome or cosmetically concerning, consulting a healthcare professional is recommended for proper diagnosis and guidance. Treatment options, including antibiotics, drainage, or surgical excision, can be explored if necessary. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their skin cysts. Remember, regular self-care practices and good hygiene can help prevent complications associated with skin cysts.
Sources
- Ovarian Cyst – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf
- Breast cysts – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic
- Skin cyst – NHS
- Epidermoid cysts – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic
Medical Disclaimer
NowPatient has taken all reasonable steps to ensure that all material is factually accurate, complete, and current. However, the knowledge and experience of a qualified healthcare professional should always be sought after instead of using the information on this page. Before taking any drug, you should always speak to your doctor or another qualified healthcare provider.
The information provided here about medications is subject to change and is not meant to include all uses, precautions, warnings, directions, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or negative effects. The absence of warnings or other information for a particular medication does not imply that the medication or medication combination is appropriate for all patients or for all possible purposes.