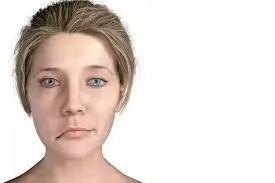
We’ve all heard of Bell’s palsy, but have you ever wondered if it’s dangerous? Seeing a friend or family member cope with this condition can be scary. Bell’s palsy affects the facial nerves, causing one side of the face to droop suddenly. It’s a condition that can have an impact on a person’s daily life and self-esteem.
In this article, we’ll explore what Bell’s palsy is and whether it poses any serious risks. We’ll also look into how doctors diagnose and treat this condition. Plus, we’ll discuss Bell’s palsy symptoms and what it’s like to live with this condition. By the end, you’ll have a better understanding of Bell’s palsy and how to handle it if it affects you or someone you care about.
What is Bell’s Palsy?
Definition
Bell’s palsy is a condition that has an impact on the facial nerves, causing temporary weakness or paralysis of the muscles on one side of the face. This results in a drooping appearance, making it challenging to make full facial expressions. The condition gets its name from Sir Charles Bell, a Scottish surgeon who first described it in the 19th century. Bell’s palsy can affect anyone at any age, but it’s most common in people between 15 and 60 years old, with an average onset age of 40.
Symptoms of Bell’s palsy
The main sign of Bell’s palsy is sudden facial muscle weakness or paralysis, usually on one side. Symptoms typically appear within 48 to 72 hours and can range from mild weakness to complete paralysis. People with Bell’s palsy may experience difficulty wrinkling their forehead, blinking, or making facial expressions on the affected side. Other symptoms can include drooling, dry eyes, trouble speaking or eating, facial or ear pain, headache, loss of taste, and increased sensitivity to sounds. In rare cases, Bell’s palsy can affect both sides of the face.
Causes
While the exact cause of Bell’s palsy isn’t always clear, it’s often related to inflammation and compression of the seventh cranial nerve. This nerve controls facial movements and expressions, as well as taste and tear production. Several viral infections may trigger this inflammation, including herpes simplex 1, varicella-zoster virus, Epstein-Barr virus, and COVID-19. Other potential triggers include a weakened immune system due to stress, illnesses, sleep deprivation, physical trauma, or autoimmune conditions. However, in many cases, healthcare providers can’t identify a specific trigger for Bell’s palsy.
Is Bell’s Palsy dangerous?
While Bell’s palsy can be alarming, it’s generally not considered dangerous. Most cases resolve on their own within a few weeks to six months. However, it’s important to understand the potential risks and complications associated with this condition.
Short-term risks
The immediate concern with Bell’s palsy is protecting the affected eye. Since the condition can make it difficult to close the eye on the affected side, it’s essential to take steps to prevent cornea dryness and potential vision loss. We need to keep the eye moist and protected to avoid complications.
Another short-term risk is the similarity of Bell’s palsy symptoms to those of a stroke. It’s vital to see a healthcare provider immediately if you notice sudden facial weakness. While Bell’s palsy isn’t life-threatening, a stroke is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention.
Long-term complications
For most people, Bell’s palsy is temporary. About 80% of people fully recover within three months. However, some may experience long-lasting effects. The risk of permanent facial weakness increases with age, especially for those over 60, and is higher in cases of complete facial paralysis.
In rare cases, long-term complications can occur. These may include synkinesis, where nerve fibres regrow incorrectly, causing involuntary facial movements. For example, your eye might water when you eat, or your mouth might twitch when you blink. Some people may also experience changes in taste or excessive tearing.
Recent studies suggest a potential link between Bell’s palsy and an increased risk of non-hemorrhagic stroke. This connection might be related to the herpes simplex virus, which has been linked to both conditions.
While Bell’s palsy isn’t typically dangerous, it’s important to seek prompt medical attention and follow treatment recommendations to minimise potential complications and ensure the best possible recovery.
Diagnosis and treatment
Medical evaluation
A healthcare provider will conduct a thorough medical evaluation of various facial expressions, such as closing your eyes, lifting your brows, and showing your teeth. This helps assess the extent of facial muscle weakness.
Blood tests will be carried out to check for infections like Lyme disease. Electromyography (EMG) is another test that measures nerve activity and muscle response. This can help predict the recovery timeline. In certain situations, imaging scans like CT or MRI’s might be recommended to exclude other possible causes of facial nerve compression.
Treatment options
Treatment for Bell’s palsy aims to improve facial nerve function and reduce nerve damage. Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are often prescribed to reduce inflammation and swelling of the facial nerve. This is most effective when started within 72 hours of symptom onset.
Artificial tears during the day and eye ointment at night may be recommended to prevent corneal dryness and potential damage. In some cases, an eye patch is suggested for protection.
Physical therapy, including facial exercises and massage, can be beneficial in promoting active rehabilitation. Some healthcare providers may recommend electrical stimulation, although its effectiveness is still debated.
Recovery timeline
Recovery from Bell’s palsy can vary greatly. Many see an improvement within two to three weeks, with full recovery often occurring within three to six months. However, in some cases, it may take longer. Little improvement after three weeks requires a follow-up with your healthcare provider.
Living with Bell’s Palsy
Coping strategies
Living with Bell’s palsy can be challenging, but there are ways to manage the condition and improve your quality of life:
- Take good care of your affected eye, using artificial tears during the day and a thicker eye gel at night to prevent dryness and potential damage
- Plenty of rest, eat well and try to reduce stress
- Physical therapy exercises can be beneficial. Massage and exercise your face according to a physical therapist’s advice to help relax your facial muscles
- Alternative treatments like acupuncture or biofeedback training, although scientific evidence for these methods is limited
To manage facial pain, we can use over-the-counter pain relievers like aspirin or ibuprofen. Applying moist heat to our face several times a day may also help reduce discomfort.
Conclusion
Bell’s Palsy, while often alarming, typically doesn’t pose serious dangers. Most people recover fully within a few months, but it’s crucial to protect the affected eye and seek medical attention. Understanding the condition, its symptoms, and treatment options can help ease concerns and improve the recovery process.
Living with Bell’s Palsy can be challenging but remember it’s usually temporary, and with proper care and patience, most of us can look forward to a full recovery.
Sources
- Bell’s Palsy: What It Is, Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
- Bell’s palsy – NHS
- Bell’s Palsy – National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
- Bell’s Palsy – Symptoms, Causes, Treatment – NORD
- Facial Paralysis: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
Medical Disclaimer
NowPatient has taken all reasonable steps to ensure that all material is factually accurate, complete, and current. However, the knowledge and experience of a qualified healthcare professional should always be sought after instead of using the information on this page. Before taking any drug, you should always speak to your doctor or another qualified healthcare provider.
The information provided here about medications is subject to change and is not meant to include all uses, precautions, warnings, directions, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or negative effects. The absence of warnings or other information for a particular medication does not imply that the medication or medication combination is appropriate for all patients or for all possible purposes.