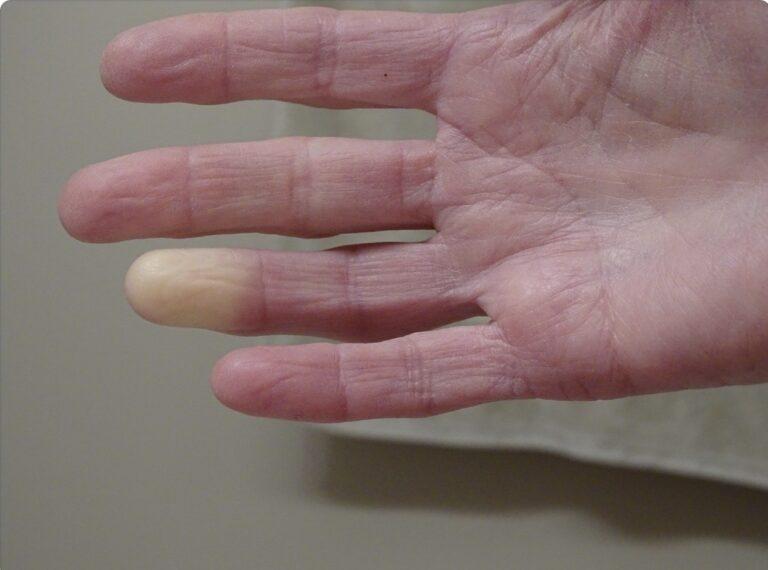
Raynaud’s disease, also known as Raynaud’s phenomenon or Raynaud’s syndrome, is a condition that affects the blood supply to certain parts of the body, particularly the fingers and toes. It is characterized by episodes of vasospasm, where the small arteries that supply blood to these areas narrow, resulting in symptoms such as numbness, coldness, and color changes in the skin. While Raynaud primarily affects the extremities, there have been concerns about its impact on the heart and cardiovascular health. In this article, we will explore the relationship between Raynaud’s disease and the heart, including any potential effects on cardiovascular function and the management of these concerns.
Understanding Raynaud’s disease
Before delving into the impact on the heart, it is important to have a clear understanding of Raynaud’s disease. There are two types of Raynaud’s disease: primary and secondary. Primary Raynaud’s disease is the most common form and occurs without an underlying cause. Family history appears to increase the risk of primary Raynaud’s. It typically manifests in individuals who are otherwise healthy and often starts in the teenage years or early adulthood.
Secondary Raynaud’s, on the other hand, is associated with an underlying condition or trigger, such as autoimmune diseases like scleroderma or lupus, side effects of certain medications, or exposure to certain substances. It also can result from blood vessel damage due to injury, frostbite or the use of jarring machinery, such as jackhammers or chainsaws.
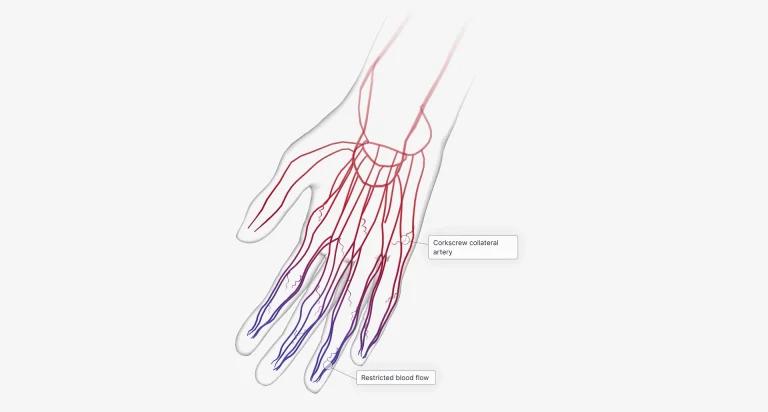
During an episode of Raynaud’s, the affected areas, usually the fingers and toes, may turn white, then blue, and finally red as blood flow returns. This occurs due to the constriction/reduced blood flow and subsequent relaxation of the small arteries that supply blood to these areas. The episodes are often triggered by exposure to cold temperatures or emotional stress, and the symptoms of Raynaud can range from mild to severe, with some individuals experiencing pain, tingling, or even ulcers in severe cases. While Raynaud primarily affects the extremities, it is important to consider its potential impact on other parts of the body, including the heart.
Some drugs that can induce Raynaud’s include beta blockers generally prescribed for high blood pressure, migraine medications containing ergotamine or sumatriptan, ADHD medications and some chemotherapy drugs. In addition, some medical conditions can trigger Raynaud’s phenomenon, such as connective tissue disease, rheumatoid arthritis, symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome and Sjogren’s syndrome.
The relationship between Raynaud’s and the heart
When it comes to the impact of Raynaud’s disease on the heart, there is limited evidence suggesting a direct connection. Primary Raynaud’s, in particular, is not known to directly affect the heart. However, individuals with Raynaud’s disease, regardless of the type, may have an increased risk of developing certain cardiovascular conditions or experiencing complications related to the heart.
Cardiovascular risk factors
One reason for the potential association between Raynaud’s disease and cardiovascular issues is the presence of shared risk factors. For example, individuals with Raynaud’s may be more likely to have other risk factors for heart disease, such as smoking, a sedentary lifestyle, or underlying conditions like hypertension or high cholesterol levels. It is important for individuals with Raynaud’s to be aware of these risk factors and take appropriate measures to manage them.
Vascular function and endothelial dysfunction
Another area of interest is the potential impact of Raynaud’s disease on vascular function and endothelial dysfunction. The endothelium, which lines the inner walls of blood vessels, plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy blood flow and regulating vascular tone. Dysfunction of the endothelium can contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases. Some studies have suggested that individuals with Raynaud’s disease may have impaired endothelial function, which could have implications for overall cardiovascular health. However, more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between Raynaud’s and endothelial dysfunction.
Raynaud’s and other cardiovascular conditions
In addition to the potential impact on vascular function and endothelial health, Raynaud’s disease may be associated with an increased risk of certain cardiovascular conditions. For example, individuals with Raynaud’s, particularly secondary Raynaud’s, may have a higher prevalence of conditions like scleroderma or lupus, which are known to affect the heart and blood vessels. These underlying conditions can increase the risk of developing heart-related complications.
Diagnosis and evaluation
If you have symptoms of Raynaud’s disease and are concerned about its potential impact on your heart, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and evaluation. The healthcare provider will typically assess your medical history, conduct a physical examination, and may order additional tests to evaluate your cardiovascular health.
- Medical History: Providing detailed information about your symptoms, triggers, and any existing medical conditions will help your healthcare provider in the diagnosis and evaluation process. Be prepared to discuss any chest pain, shortness of breath, or other cardiovascular symptoms you may have experienced
- Physical Examination: During a physical examination, your healthcare provider may assess your blood pressure, check for signs of reduced blood flow in the extremities, and listen to your heart and lungs for any abnormalities
- Diagnostic Tests: In some cases, additional diagnostic tests may be recommended to evaluate the impact of Raynaud’s on your heart. These tests may include:
Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG): This non-invasive test records the electrical activity of your heart and can help detect any abnormal rhythms or signs of reduced blood flow to the heart
Echocardiogram: An echocardiogram uses ultrasound waves to create images of the heart’s structure and function. It can provide valuable information about the heart’s pumping ability, valves, and overall health
Stress Tests: Stress tests are performed to evaluate how the heart responds to physical activity or stress. This test may involve exercising on a treadmill or receiving medication that simulates the effects of exercise on the heart
Cardiac Catheterization: In some cases, a cardiac catheterization may be recommended to obtain more detailed information about the blood flow in your heart. During this procedure, a thin tube is threaded through a blood vessel and into the heart to measure pressure and assess the blood vessels’ condition
Blood tests: Antinuclear antibody (ANA) test to look for arthritic and autoimmune conditions that may cause Raynaud phenomenon
Management and prevention
While the direct impact of Raynaud’s disease on the heart may be limited, it is still important for individuals with Raynaud’s to take steps to promote heart health and manage any associated risk factors. This includes adopting healthy lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding tobacco use. Managing stress levels, maintaining a warm environment and avoiding cold weather can also help minimize the frequency and severity of Raynaud’s attacks.
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage Raynaud’s symptoms or underlying conditions that contribute to the disease. These medications may include calcium channel blockers or vasodilators which help relax and widen blood vessels, or medications targeting the underlying autoimmune conditions. It is important for individuals with Raynaud’s to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs.
Regular monitoring of cardiovascular health is also essential for individuals with Raynaud’s disease, especially if they have other risk factors or underlying conditions. This may involve routine check-ups, blood pressure monitoring, cholesterol level checks, and other relevant tests as recommended by a healthcare professional.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while Raynaud’s disease primarily affects the extremities, there is a potential association between Raynaud’s and cardiovascular health. Individuals with Raynaud’s, particularly those with secondary Raynaud’s or underlying conditions, may have an increased risk of developing complications. These complications can include conditions such as hypertension, coronary artery disease, heart attack and even heart failure. However, the direct impact of Raynaud’s on the heart is limited, and more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between the two. It is important for individuals with Raynaud’s to focus on overall heart health by managing risk factors, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and working closely with their healthcare provider to develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Sources
- Raynaud’s Syndrome: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment – Cleveland Clinic
- Autonomic nervous system activity in primary Raynaud’s phenomenon: Heart rate variability, plasma catecholamines and [123I]MIBG heart scintigraphy – PMC
- Raynaud’s phenomenon – Illnesses & conditions – NHS inform
- Raynaud Syndrome – Heart and Blood Vessel Disorders – MSD Manual Consumer Version
Medical Disclaimer
NowPatient has taken all reasonable steps to ensure that all material is factually accurate, complete, and current. However, the knowledge and experience of a qualified healthcare professional should always be sought after instead of using the information on this page. Before taking any drug, you should always speak to your doctor or another qualified healthcare provider.
The information provided here about medications is subject to change and is not meant to include all uses, precautions, warnings, directions, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or negative effects. The absence of warnings or other information for a particular medication does not imply that the medication or medication combination is appropriate for all patients or for all possible purposes.